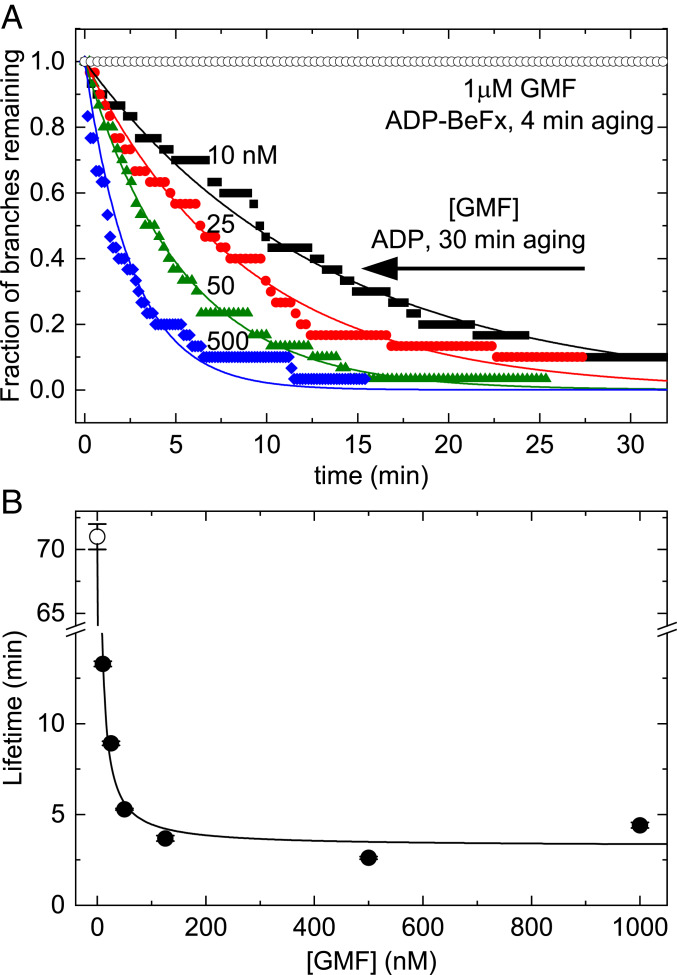
Fig. 3.
BeFx inhibits debranching by GMF. (A) Dependence of the time course of dissociation of branches with ADP−BeFx−Arp2/3 complex or ADP−Arp2/3 complex on the concentration of GMF. Branches with ADP−BeFx−Arp2/3 complex were assembled in buffer containing 0.2 mM ATP, 2 mM BeSO4, and 10 mM NaF and aged for ∼4 min. Branches with ADP−Arp2/3 complex were assembled in buffer with 0.2 mM ATP and aged for 30 min to allow for ATP hydrolysis and phosphate dissociation (Fig. 2B). Debranching was initiated by flowing buffer with GMF at 15 μL⋅min−1 and continued throughout the debranching measurements. The smooth curves are the best fits of single exponentials to the data, yielding the (average) branch lifetimes; n = 30 branches for each trace. A concentration of 1 μM GMF did not dissociate branches with ADP−BeFx−Arp2/3 complex assembled from ATP-actin and ATP−Arp2/3 complex with BeFx and aged for ∼4 min (open black circles). (B) Dependence of the lifetimes of branches with ADP−Arp2/3 complex on the concentration of GMF at a buffer flow rate of 15 μL⋅min−1. The line is the best fit of Eq. 3 to the data, yielding a GMF binding affinity (Kd,GMF) of 40 (±10) nM and a maximum debranching rate constant (kdiss,GMF) of 0.31 (±0.05) min−1. At this low flow rate, branches with ADP−Arp2/3 complex (without GMF) dissociated with a rate constant (kdiss,0 = 0.014 ± 0.0002 min−1, indicated by an open circle) similar to that under zero force (Fig. 2B and Table 1). The uncertainty bars are within the data points and represent the SDs of lifetimes in the best single exponential fits of time traces in A.