FIGURE 1.
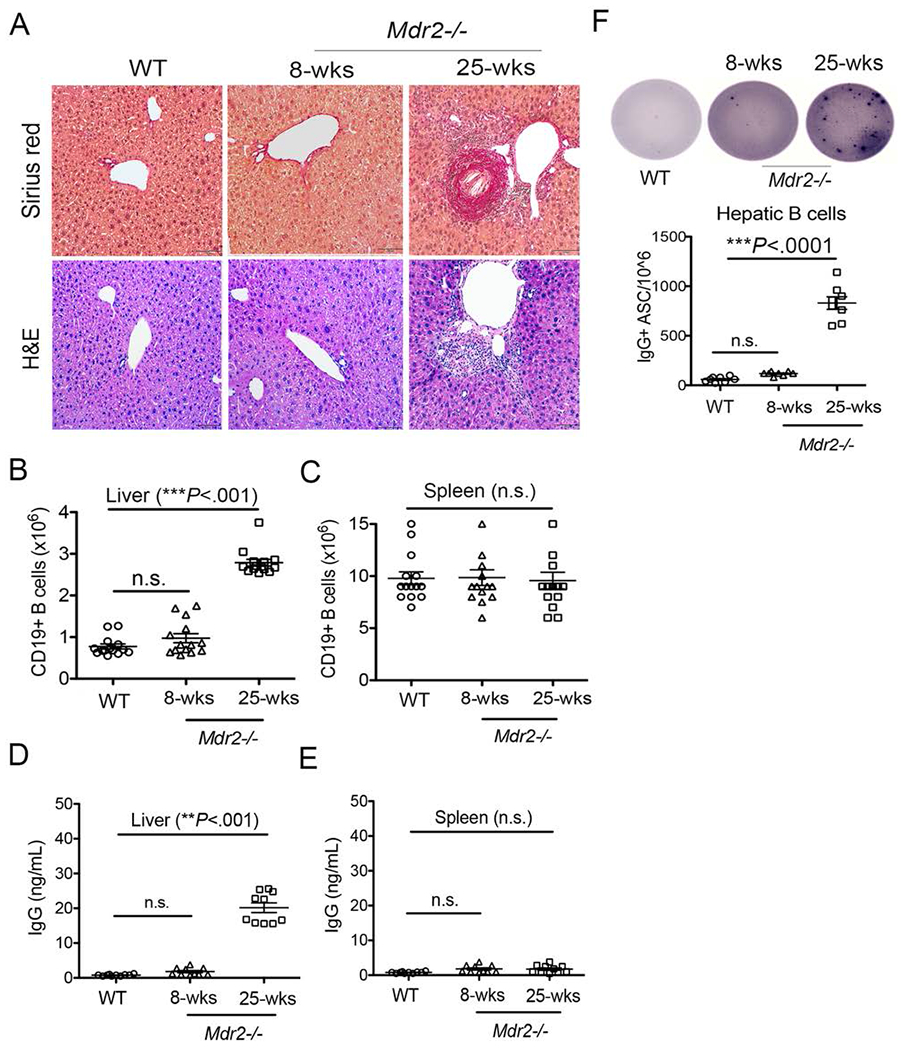
Aberrant IgG production during hepatic fibrosis. (A) Upon animal sacrifice, liver specimens from 8-weeks old and 25-weeks-old WT and Mdr2−/− mice were collected, fixed overnight in 10% formalin, and processed for histological analysis. Representative liver sections stained with Sirius red and H&E staining (Mag. 100×). are shown. (B-C) Total number of intrahepatic B lymphocytes (CD19+MHCII+) in the livers (B) and spleens (C) of WT and Mdr2−/− mice are shown. (D-E) B lymphocytes were purified and enriched using CD19 microbeads from the livers (D) and spleens (E) of WT and Mdr2−/− mice, and cultured (2 ×105 cells) in a complete IMDM medium without any stimulation for 5 days. Culture supernatants were collected and processed for total IgG detection using a standard ELISA technique. (F) Purified B lymphocytes (50,000 cells) were added to the culture plate coated overnight with anti-mouse IgG antibody and total IgG+ antibody secreting cells (IgG+ ASC/106) were detected using ELISpot technique. Data are representative of more than 3 independent experiments with 3-5 mice per group. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Mann-Whitney Test, *P<.05, **P<.001, ***P<.0001. Error bars reflect the SEM.
