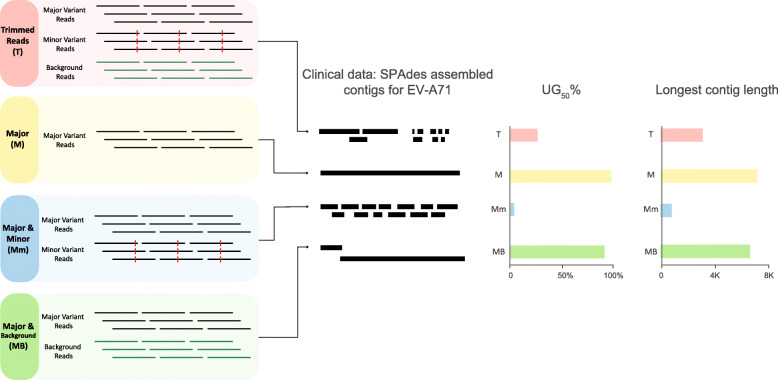
Fig. 5.
The effect of variant interference in a real dataset from a clinical sample containing enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) and its variants. Fastq reads were partitioned into four components: trimmed reads after quality control (T), major variant (M), minor variant (m), and background (B). These reads were then combined into four different experiments: T, M, Mm, and MB and assembled using SPAdes. The contig representation schematic showing the abundance and length of the generated contigs reveals the impact of variant interference on de novo assembly. The bar graphs show the UG50% metric and the length of the longest contig. UG50% is a percentage-based metric that estimates length of the unique, non-overlapping contigs as proportional to the length of the reference genome [24]. Unlike N50, UG50% is suitable for comparisons across different platforms or samples/viruses. More clinical samples and viruses are analyzed similarly in Fig. 6