FIG 1.
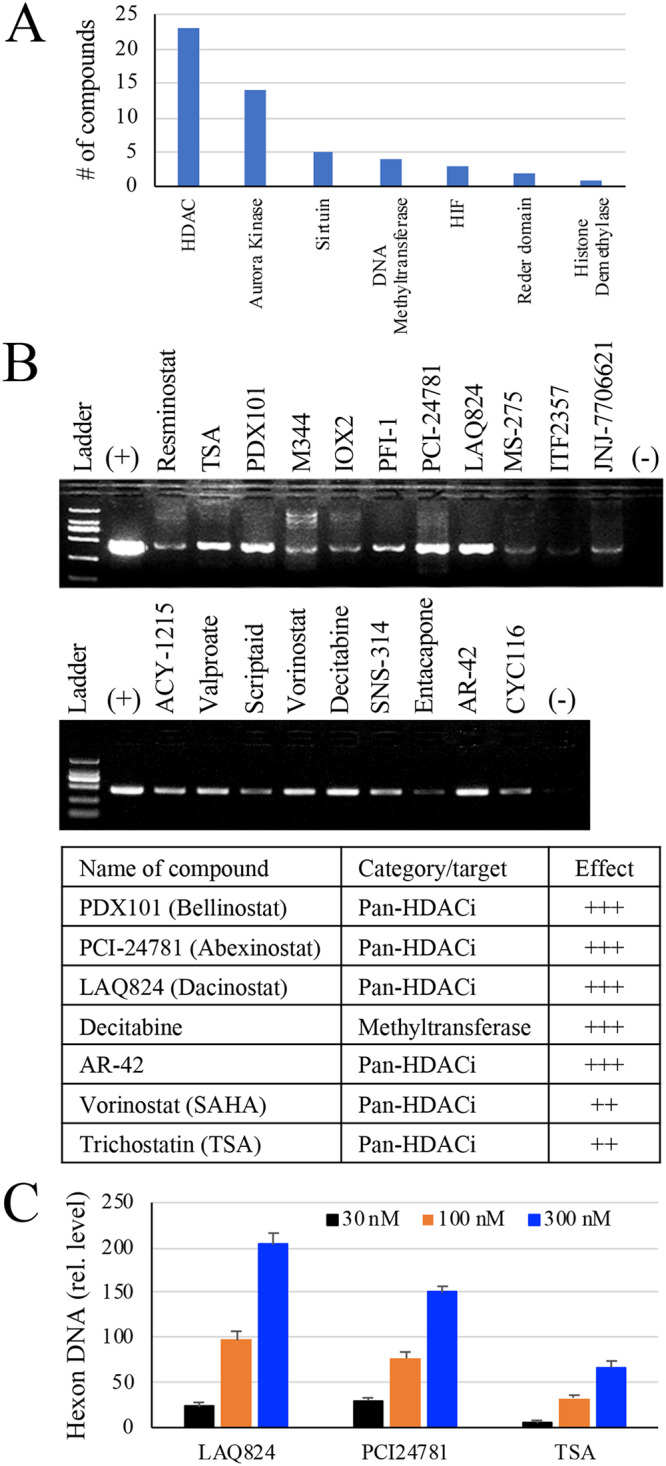
PCR results from epigenetic compound library screening. (A) The primary categories of the epigenetic informer compounds tested. (B) Compound screening on isolated tonsil lymphocytes. Tonsil lymphocytes were first examined for the presence of HAdV DNA using a pair of primers that anneal to the hexon gene of species B, C, D, and E HAdV. HAdV-positive lymphocytes in 96-well plates were vehicle treated (0.1% DMSO in culture medium) or treated with a compound for approximately 48 h. The cells and culture medium were collected and used for the detection of HAdV by PCR. The induction of HAdV DNA accumulation in the treated samples was demonstrated by PCR analysis and verified using 3 different tonsil samples. The PCR result from a representative experiment is presented, and compounds that showed more potent effects were listed. +, positive control for the PCR. (C) Dose effect of HDACi on HAdV reactivation. HAdV2-positive tonsil lymphocytes were treated with various doses of PCI24781, LAQ824, or TSA. The cells and culture medium were collected 48 h later and used for detection of HAdV2 hexon DNA by qPCR. The data were normalized against GAPDH in the samples and plotted as relative abundance against vehicle-treated controls.
