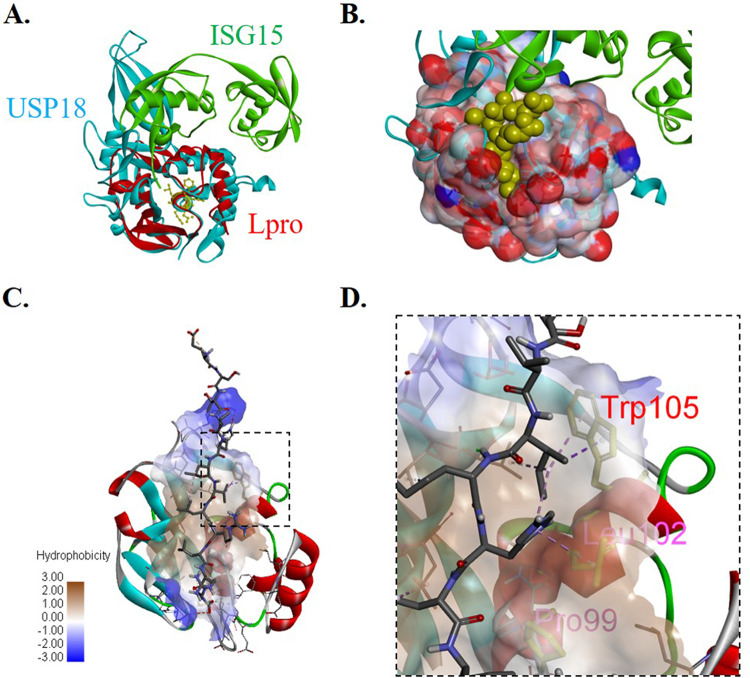
FIG 1.
Structural analysis of FMDV Lpro and ISG15 binding interface. (A) Superimposition of Lpro (PDB number 1QBB) and USP18 cocrystalized with ISG15 (PDB number 5CHV) using catalytic residues as tether points highlights structural homology. (B) Simulated surface of Lpro shows potential binding cleft for ISG15 based on superimposition with USP18. (C) Image of peptide docking results showing putative binding mechanism between ISG15 C-terminal peptide and Lpro binding pocket rendered as ribbons. (D) Close-up interactions between aromatic amino acid Trp/W 105 in red and ISG15 C-terminal peptide, rendered as a stick. Other hydrophobic interactions are highlighted in magenta, namely Pro/P 99 and Leu/L 102. All images were rendered in Discovery Studio Visualizer.