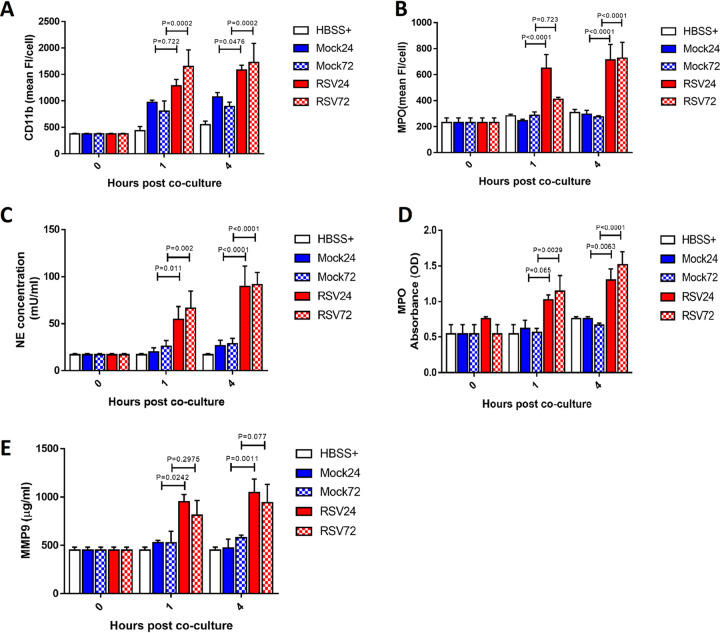
FIG 5.
Neutrophil activation and release of neutrophil-derived products and neutrophil activation after exposure to RSV-infected ciliated epithelial cells. Activation marker expression was calculated by staining for cell surface expression of CD11b (PEhi) or MPO (allophyocyanin [APC+]) and determined by flow cytometry. Neutrophils were identified using a PE-positive gate. Using this population, the geometric mean fluorescence intensity of PE or APC fluorescence was calculated. (A) Neutrophils exposed to RSV (red bars)-infected epithelial cells infected for 24 h (plain bars) or 72 h (checkered bars) show increased cell surface expression of CD11b compared to those exposed to mock (blue bars)-infected epithelial cells. (B) Neutrophils exposed to RSV (red bars)-infected epithelial cells infected for 24 h (plain bars) or 72 h (checkered bars) show increased cell surface expression of MPO compared to those exposed to mock (blue bars)-infected epithelial cells. Bars show means ± SEM (n = 5 to 8 epithelial donors with heterologous neutrophils). Statistical significance is shown. Apical surface medium concentrations of neutrophil elastase (NE) (C), MPO (D), and MMP-9 (E) were measured in the apical supernatant by ELISA collected following neutrophil exposure to mock- or RSV-infected (24 h [plain bars] or 72 h [checkered bars]) ciliated AECs after 1 or 4 h. For all graphs, bars represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5 epithelial donors with heterologous neutrophils for HBSS+ (white), mock-infected (blue bars), or RSV-infected (red bars) cultures. A statistical comparison between all groups was performed using a paired t test. Statistical significance is shown.