FIG 10.
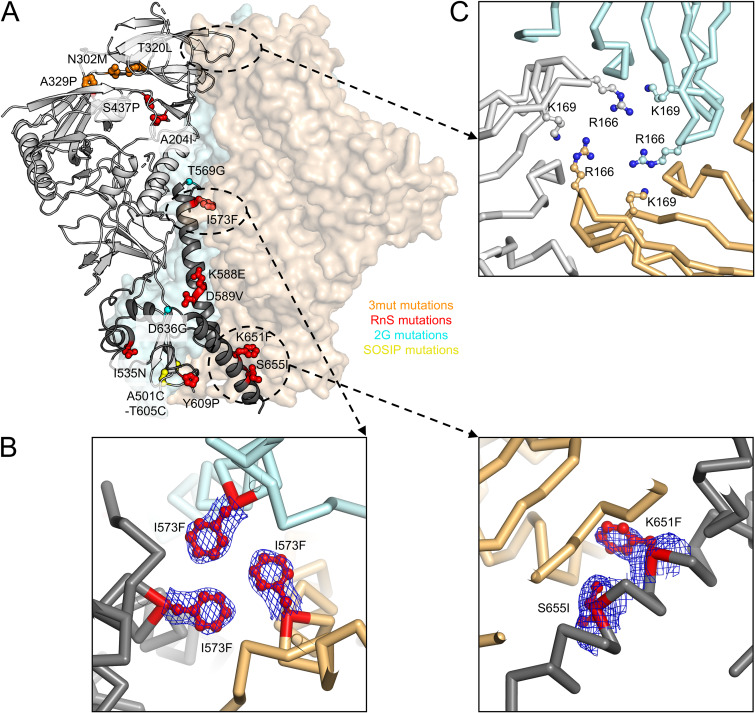
Structure of CAP256 RnS-3mut-2G-SOSIP.664 provides details on how multiple mutations stabilize a clade C soluble trimer. Previous studies have shown that CAP256 Env sequence cannot be expressed as soluble trimer by DS-SOSIP stabilization. (A) Crystal structure of the stabilized CAP256 trimer (CAP256 RnS-3mut-2G-SOSIP.664, with stabilizing mutations highlighted in stick-and-ball representation and colored according by corresponding mutation categories) in one protomer shown as ribbons (gp120 in light gray and gp41 in dark gray). The other two protomers are shown as surface representations in orange and cyan, respectively. (B) RnS mutations, highlighted in red, likely stabilize the trimerization of gp41. Electron density maps (contoured at 1.5 sigma) are shown for the mutated side chains. (C) R166 and K169 from each protomer form a positively charged patch at the trimer apex that can interact with negatively charged CDRH3 of VRC26.25 and other V1/V2 antibodies.