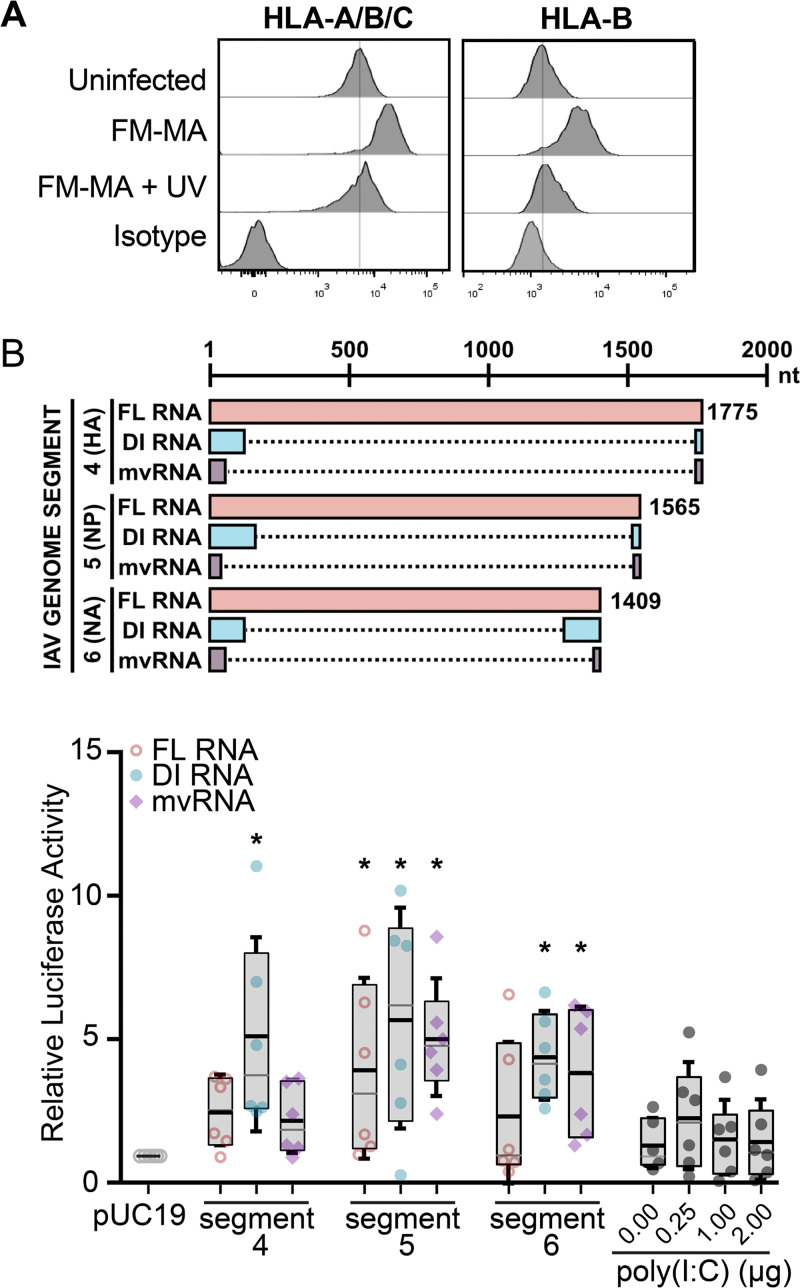
FIG 3.
Defective viral RNAs increase ISRE-dependent luciferase activity in A549 cells. (A) FM-MA inoculum was exposed to UV light prior to infection of A549 cells at MOI of 1. At 17 hpi, cells were fixed and immunostained with a pan-anti-HLA-A/B/C antibody or an anti-HLA-B antibody and processed for flow cytometry. The vertical lines indicate the HLA expression level in uninfected cells. Representative data from one out of two independent experiments is shown. (B) (Top) Cartoon compares RNAs derived from the indicated genome segments and expressed from pPolI-based minireplicon plasmids, including full-length (FL) vRNA, defective interfering (DI) vRNA, or mini-viral RNA (mvRNA); dashed lines mark internal deletions on the DI RNAs and mvRNAs. (Bottom) A549 cells were transfected with IAV minireplicons expressing the indicated FL vRNAs, DI RNAs, or mvRNAs derived from the indicated genome segments. An ISRE-driven firefly luciferase reporter plasmid was cotransfected with minireplicon plasmids to measure IFN signaling, along with a Renilla luciferase plasmid that served as normalization control. Poly(I·C) and an empty pUC19 plasmid served as positive and negative controls, respectively. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase control for each sample, and data were expressed as fold change compared with pUC19 plasmid transfection (n = 6; *, P < 0.05; IQR boxes and SD whiskers are shown).