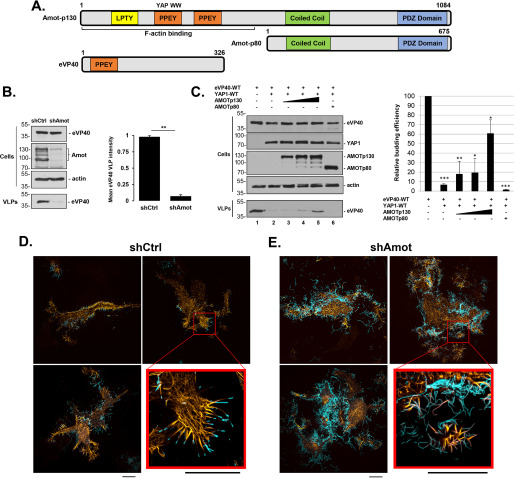
Figure 1.
eVP40 VLP budding from shCtrl or shAmot cells. A, schematic diagrams of full-length Amot-p130, N-terminally truncated isoform Amot-p80, and eVP40 with key domains highlighted. Both the PPEY motif that binds to the WW-domain of YAP and the F-actin–binding domain of Amot-p130 are indicated. Numbers represent amino acids. B, representative Western blotting for eVP40 VLP budding assay in shCtrl and shAmot cells (0.25 µg of eVP40 plasmid/transfection). The indicated proteins were quantified in cells and VLPs using National Institutes of Health ImageJ software. The bar graph represents data from at least three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01. C, representative Western blotting for YAP1 inhibition and Amot-p130 rescue of eVP40 VLP budding. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of plasmids (0.25 µg of eVP40; 0.25 µg of YAP1-WT; 0.25, 0.5, or 1.0 µg of Amot-p130; and 1.0 µg of Amot-p80). The indicated proteins were quantified in cells and VLPs using National Institutes of Health ImageJ software. The bar graph represents data from at least three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. shCtrl (D) or shAmot cells (E) were transfected with 0.5 µg each of pCMV-LifeAct-RFP and YFP-eVP40 plasmids, and cells were imaged by SIM-TIRF microscopy at 24 h post-transfection. Three representative images of F-actin (yellow) and YFP-eVP40 (cyan) are shown along with an enlarged view of the area indicated by a red box. All scale bars, 10 μm. Error bars, S.D.