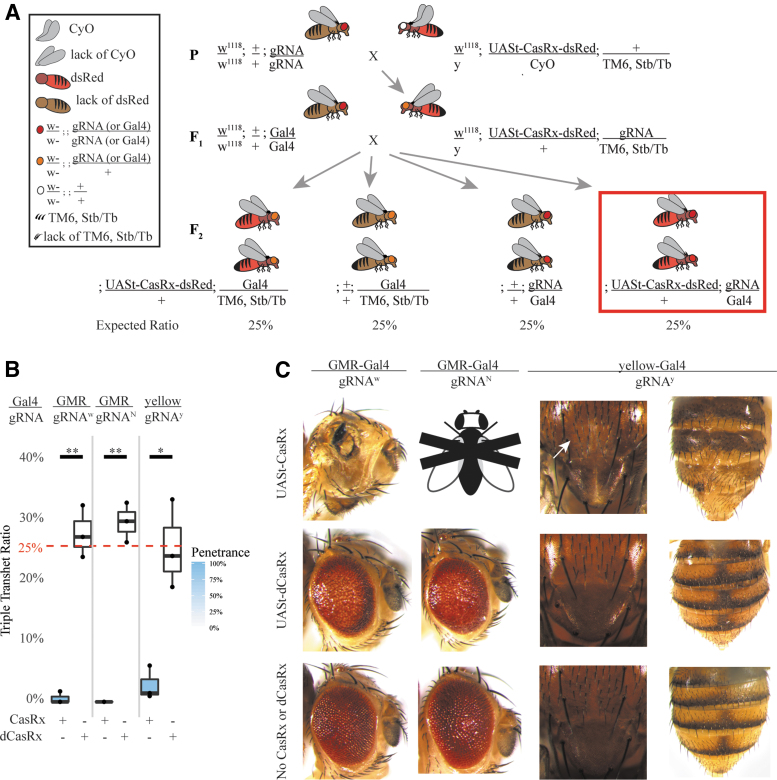
Fig. 2.
Genetic assessment of programmable CasRx-mediated transcript reduction in flies. (A) Representative genetic crossing schematic to generate transheterozygotes. (B) Inheritance and penetrance rates of transheterozygous flies inheriting both Ubiq-CasRx (or Ubiq-dCasRx) and gRNAarray corresponding to the red box in panel A. Phenotype penetrance rate is depicted by blue shading in the box plot. Significant differences in inheritance between CasRx and dCasRx groups were observed in all three groups (P values: gRNAw = 0.00135; gRNAN = 0.00006; gRNAy = 0.00016). (C) Brightfield images of transheterozygous flies with representative phenotypes for each cross. Corresponding genotype for each image is dictated by the combination of constructs on top of the columns and the side of the rows. Arrows point to tissue necrosis in the eye. Black and white fly with “X” represents lethality phenotype where no transheterozygote adults emerged. dCasRx, catalytically inactive negative control CasRx.