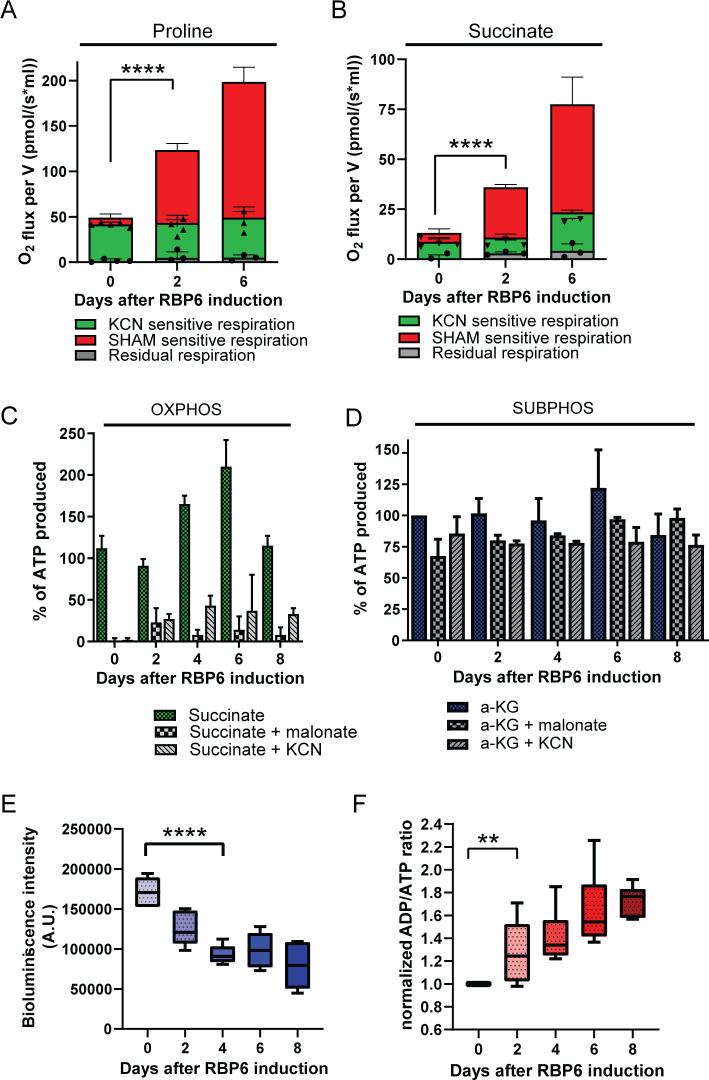
Fig 8. Changes in cellular respiration and mitochondrial ATP production in RBP6OE cells.
(A, B) Oxygen consumption rates in the presence of 5 mM proline (A) or 5 mM succinate (B) in live or digitonin-permeabilized cells, respectively. Respiration via AOX was monitored in the presence of KCN (0.5 mM). Individual values shown as dots (means ± SD, n = 3–5). ****P < 0.0001. (C, D) The in vitro ATP production by oxidative or substrate phosphorylation (OXPHOS, SUBPHOS) measured in digitonin-extracted mitochondria from uninduced and RBP6-induced cells. The phosphorylation pathways are triggered by the addition of ADP and by succinate (C) or α-ketoglutarate (a-KG, D). Malonate (mal.) and KCN, specific inhibitors of succinate dehydrogenase and complex IV are used to inhibit ATP production by OXPHOS. The levels of ATP production in mitochondria isolated from uninduced RBP6OE cells are established as the reference and set to 100% (means ± SD, n = 2–4). (E) Cellular ATP content in RBP6OE cells. (means ± SD, n = 6, ****P < 0.0001). (F) Relative ADP/ATP ratios of RBP6OE cells. The ADP/ATP ratio in uninduced RBP6OE cells (between 1.75 and 6.01) is established as a reference and set to 1. In T. brucei, ADP/ATP ratio reaches unusually high levels, as also reported elsewhere [44]. The measured values are shown in S1 Data (means ± SD, n = 6–10, **P < 0.01). Underlying data plotted in panels A, B, C, D, E, and F are provided in S1 Data. AOX, alternative oxidase; KCN, potassium cyanide; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; RBP6, RNA binding protein 6; SHAM, salicylhydroxamic acid; SUBPHOS, substrate phosphorylation.