Table 1.
Full list of notation and parameter values used
| Parameter | Explanation | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
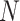
|
Population size |
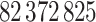
|
individuals |
|
Individual birth rate |
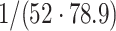
|
week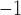
|
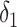
|
Aging from age group 1 (age 0–4) to 2 (age 5–59) |
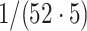
|
week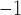
|
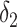
|
Aging from age group 2 (age 5–59) to 3 (age 60+) |
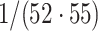
|
week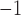
|
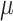
|
Death rate (from age group 3 (age 60+) ) |
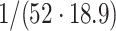
|
week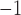
|
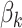
|
Susceptibility of age group 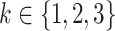
|
To be estimated | individuals/week |
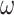
|
Immunity waning rate |
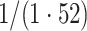
|
week
|
|
Recovery rate |
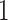
|
week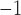
|
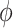
|
Phase shift of the seasonal forcing | To be estimated | 1 |
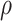
|
Amplitude of the seasonal forcing | To be estimated | 1 |
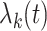
|
Force of infection of age group 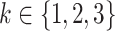
|
Defined by Eqn. (3.3) | individuals/week |
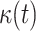
|
Seasonal forcing function | Defined by Eqn. (3.4) | 1 |
|
Overdispersion parameter | To be estimated | 1 |
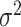
|
Scale parameter of the 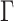 -noise -noise |
To be estimated | 1 |
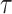
|
Time step | To be estimated | week |
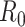
|
Basic reproduction number | To be estimated | individuals |
The inverse of the yearly birth rate equals the sum of the inverses of the yearly aging and death rates which add up to 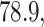 which is the total life expectancy at birth in Germany averaged between the years 2001 and 2008, taken from The World Bank (2016). The averaged population size
which is the total life expectancy at birth in Germany averaged between the years 2001 and 2008, taken from The World Bank (2016). The averaged population size 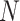 in Germany during that time period is taken from Statistisches Bundesamt (2016) and the reporting interval is 1 week. As in Atkins and others (2012), we assume that all individuals are immune against rotavirus for an average of one year. A more detailed discussion on the choice of this assumption can be found in Section 7.
in Germany during that time period is taken from Statistisches Bundesamt (2016) and the reporting interval is 1 week. As in Atkins and others (2012), we assume that all individuals are immune against rotavirus for an average of one year. A more detailed discussion on the choice of this assumption can be found in Section 7.
