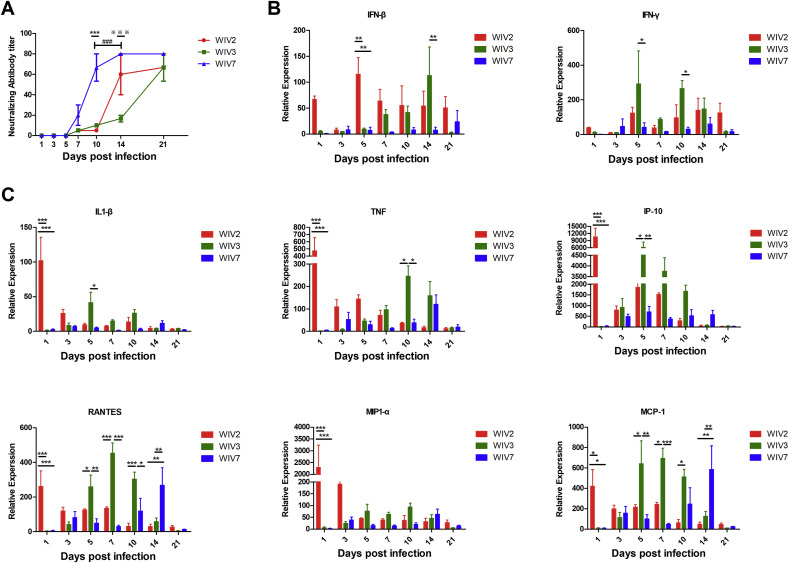
Fig. 5.
Bat MRVs induced different patterns of humoral immune response and proinflammatory gene production in BALB/c mice. Infected and mock-infected mice were euthanised at several time points, serum was separated from blood and lungs were collected. Anti-bat MRV neutralisation antibody titres were determined (A). Each serum was measured in triplicate. Titres were expressed as the reciprocal of the final serum dilution required to neutralise all inoculated wells. Total lung RNA was analysed for mRNA expression by RT-qPCR. The gene transcription levels of IFN-β, IFN-γ (B) and proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines (C) were assessed. All data were normalised to 18S rRNA. Relative expression was expressed as the relative fold increase over mock-infected mice. Error bar indicates the standard error. * represent WIV-2 group compared with WIV-7 group, # represent WIV-3 group compared with WIV-7 group, ※ represent WIV-2 group compared with WIV-3 group (A). Black underline represent the comparison between indicated groups (B and C), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.