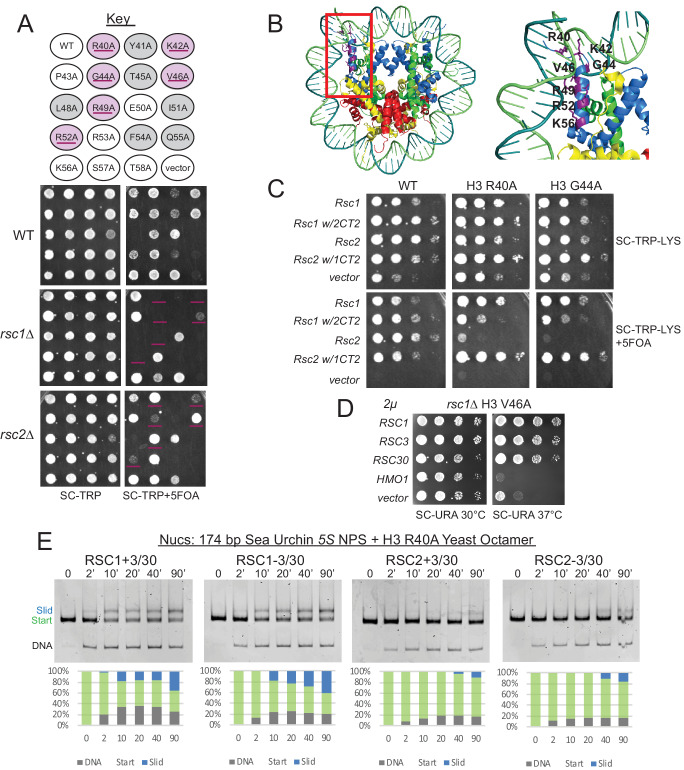
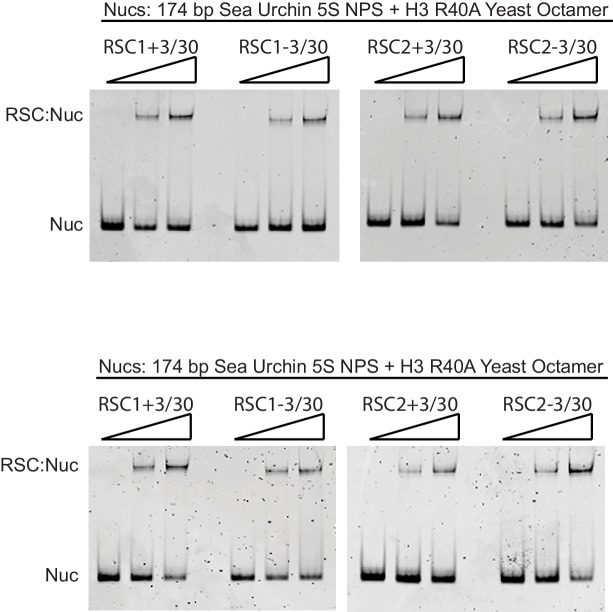
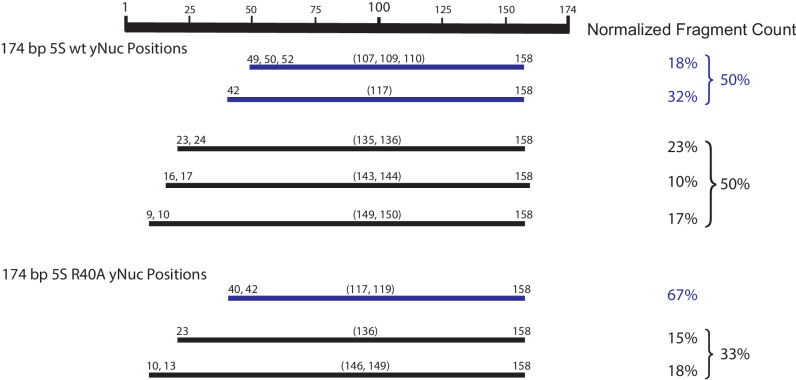
Figure 3. Mutations in the H3 αN helix are lethal in combination with rsc1∆, but not rsc2∆, and they reduce RSC remodeling of the 5S nucleosome.
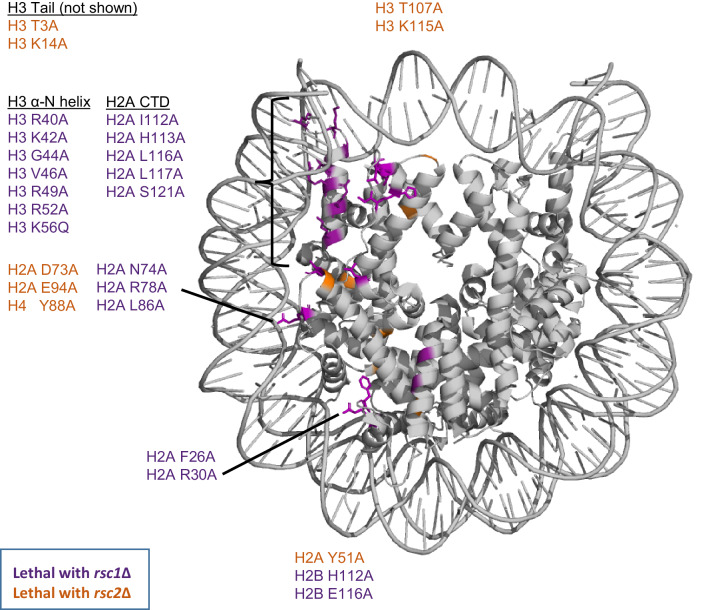
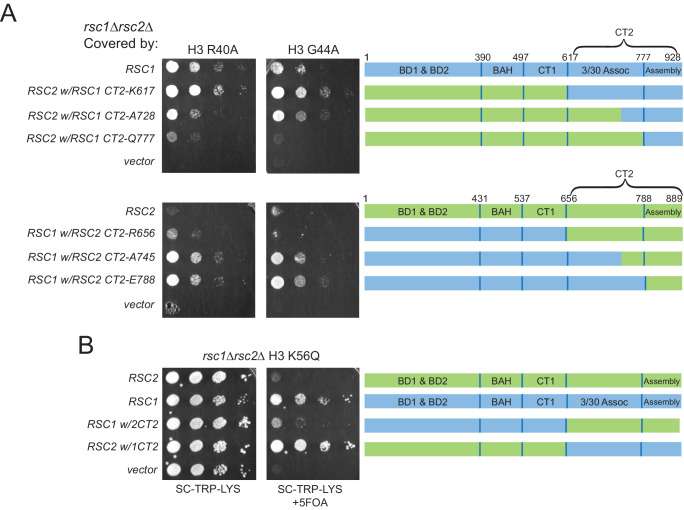
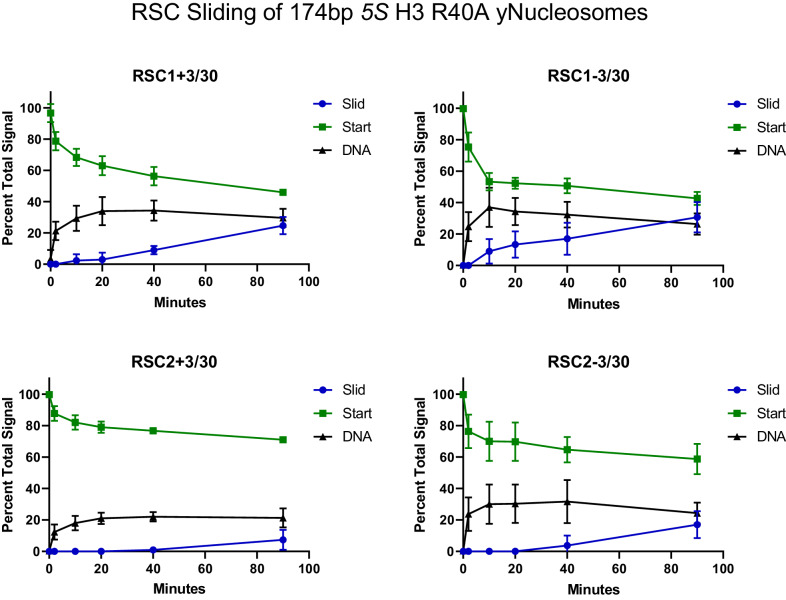
(A) Histone H3 αN helix mutations that are lethal with rsc1∆. TRP1-marked plasmids containing WT H4, and H3 mutations within the αN helix were transformed into h3-h4∆ [H3-H4.URA3] (YBC1939), rsc1∆ h3-h4∆ [H3-H4.URA3] (YBC2090) or rsc2∆ h3-h4∆ [H3-H4.URA3] (YBC3040), and spotted to SC-TRP or SC-TRP+5FOA to force the loss of the WT histone plasmid. Mutations that were lethal on their own without mutated RSC are shaded in grey. Mutations that were lethal in rsc1∆ but not rsc2∆ are shaded in purple and underlined. Transformants were grown at 30°C for 2 days. Shown is one of two biological replicates. (B) Location of the synthetic lethal rsc1∆ H3 αN helix mutations are depicted in purple on the nucleosome, PDB code 1ID3. (C) The RSC1 CT2 region complements the synthetic lethal rsc1∆ H3 αN helix mutations. rsc1∆ rsc2∆ h3-h4∆ [RSC1.URA3] with [H3.WT, R40A, or G44A-H4.WT. LYS2] (YBC3466, YBC3444, YBC3433) transformed with TRP1-marked plasmids bearing RSC1 (p609), RSC2 (p604), RSC1 w/2CT2 (p3097), RSC2 w/1CT2 (p3098), or vector (pRS314) and spotted as 10x serial dilution to SC-TRP-LYS, or SC-TRP-LYS+5FOA. Shown is one of four biological replicates. (D) High-copy RSC3 or RSC30 will partially suppress the Tsˉ phenotype of rsc1∆ H3V46A. Strain rsc1∆ h3-h4∆ [H3.V46A-H4.WT.TRP] (YBC3586) transformed with URA3-marked high copy (2μ) plasmids containing RSC1 (p705), RSC3 (p1310), RSC30 (p916), HMO1 (p3390), or vector (pRS426), and spotted as 10x serial dilutions at 30°C or 37°C. Shown is one of two biological replicates. (E) Comparative sliding and ejection of 174 bp sea urchin 5S NPS H3 R40A yeast mononucleosomes (20 nM) by RSC1 and RSC2 complexes (30 nM). The nucleosomal Start (green), Slid (blue), and free DNA (grey) bands were quantified and reported as a percent of the total signal.