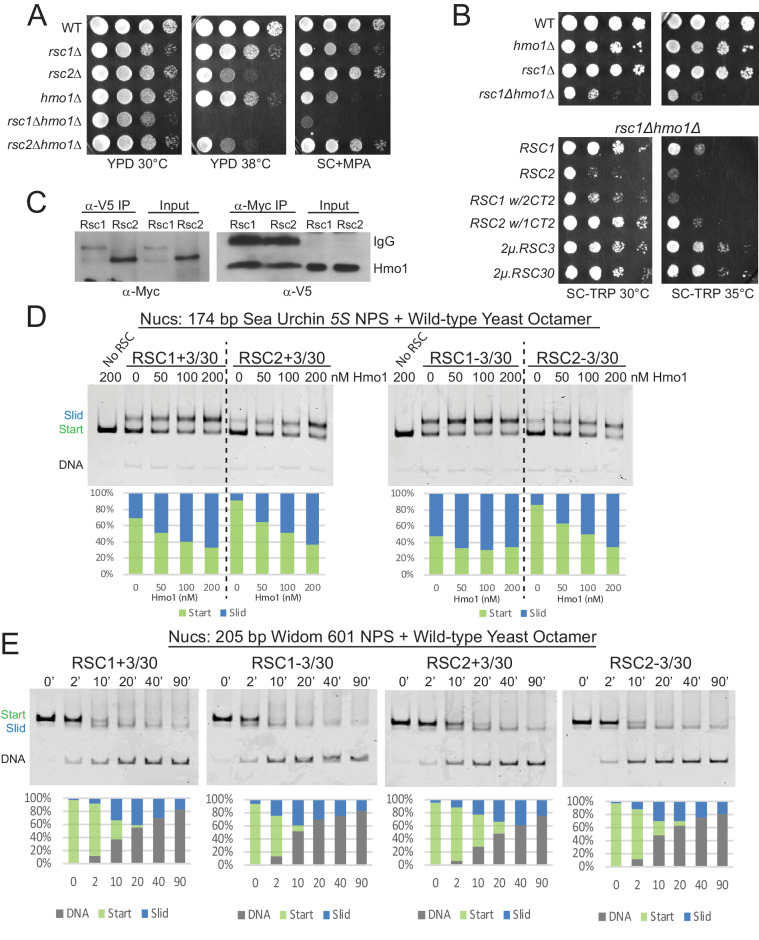
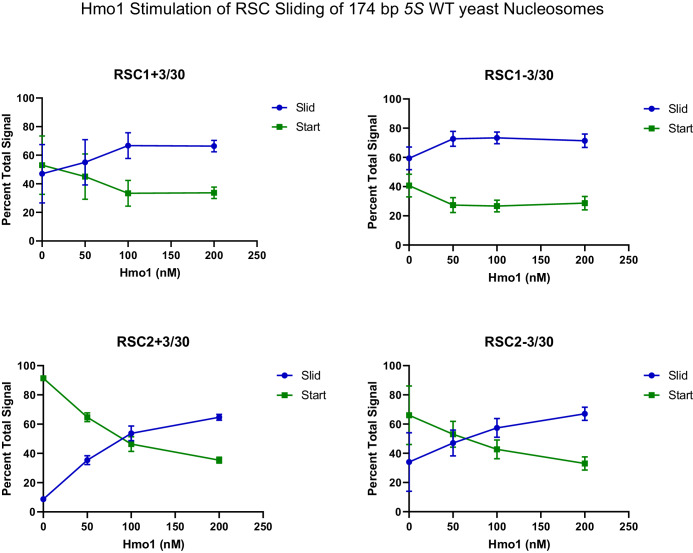
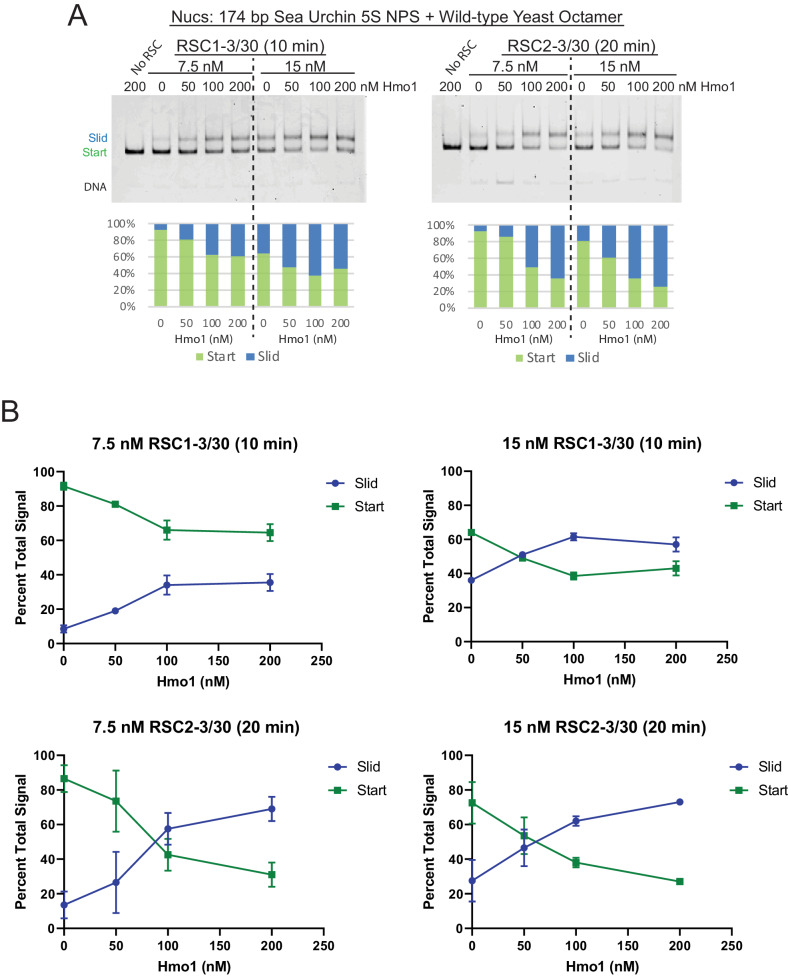
Figure 4. Hmo1 cooperates with RSC to remodel fragile or partially-unwrapped nucleosomes.
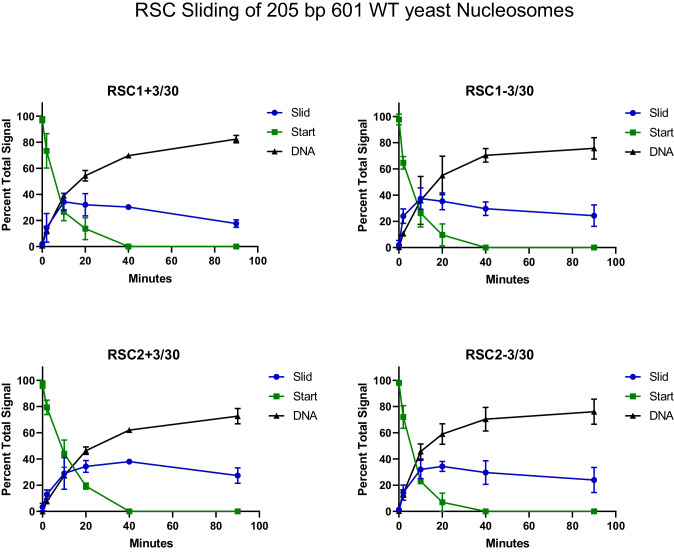
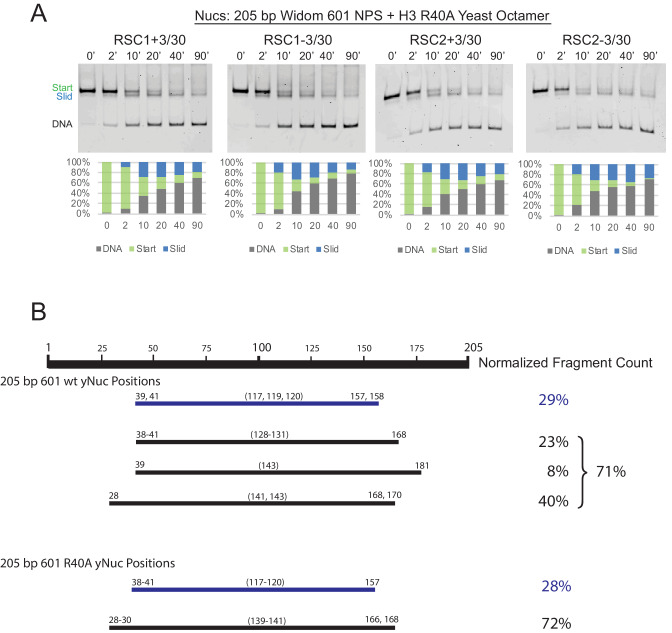
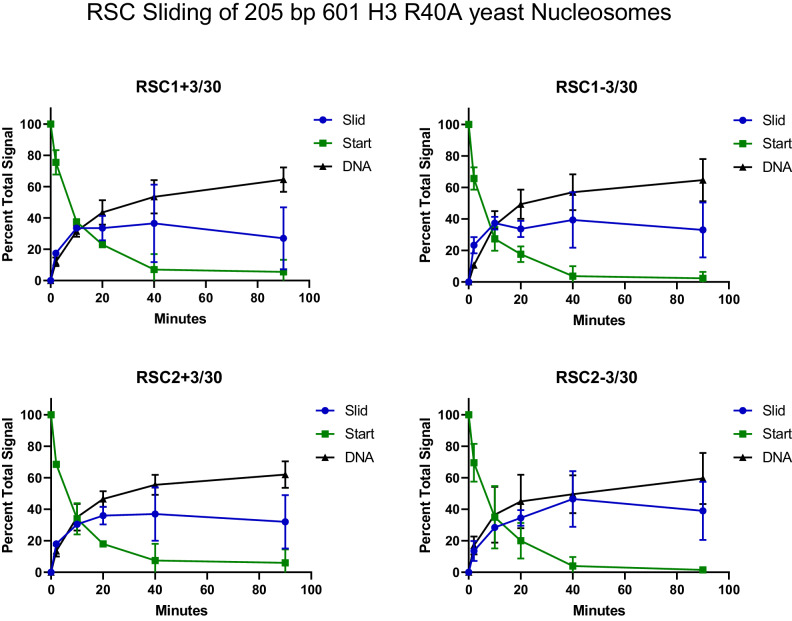
(A) An hmo1 null mutation is synthetically sick with rsc1Δ, but not rsc2Δ. WT (YBC604), rsc1Δ (YBC774), rsc2Δ (YBC82), hmo1Δ (YBC3509), rsc1∆ (YBC774), rsc2Δ (YBC82), rsc1Δ hmo1Δ (YBC3514), rsc2∆ hmo1∆ (YBC3515) spotted as 10x serial dilutions to YPD 30°C, YPD 38°C, and SC+20 µg/ml mycophenolic acid (MPA). One of two or more biological replicates shown. (B) The rsc1Δ hmo1Δ synthetic sickness is suppressed by high copy RSC3, RSC30, or RSC1 CT2. Strain rsc1∆ hmo1∆ (YBC3514) transformed with TRP1-marked RSC1 (p609), RSC2 (p604), RSC1 w/2CT2 (p3097), RSC2 w/1CT2 (p3098), 2µ.RSC3 (p929), 2µ.RSC30 (p911), or vector (pRS314) spotted as 10x serial dilutions to SC-TRP 30°C or SC-TRP 35°C. One of four biological replicates shown. (C) Co-IP of Rsc1 and Rsc2 with Hmo1. Sonicated chromatin extracts from RSC1.9XMYC HMO1.V5 (YBC3558) and RSC2.9XMYC HMO1.V5 (YBC3559) were immunoprecipitated using anti-Myc or anti-V5. Western blots were probed with anti-Myc or anti-V5 antibodies. One of three biological replicates shown. (D) Comparative sliding by RSC1 and RSC2 complexes (10 nM) of 174 bp sea urchin 5S yeast mononucleosomes (20 nM) pre-incubated with increasing concentrations of Hmo1 protein. Reactions were conducted at 30°C for 20 min. The Start (green) and Slid (blue) bands were quantified and reported as percent of the total signal. The free DNA band was negligible and not quantified. (E) Comparative sliding and ejection of Widom 601 yeast mononucleosomes (20 nM) by RSC1 and RSC2 complexes (10 nM). The nucleosomal Start (green), Slid (blue), and free DNA (grey) bands were quantified and reported as a percent of the total signal.
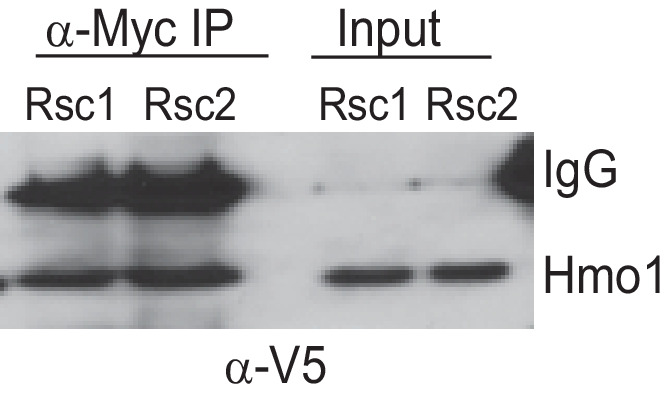
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Co-Immunoprecipitation of Rsc1 and Rsc2 with Hmo1 from MNase-treated chromatin extracts.