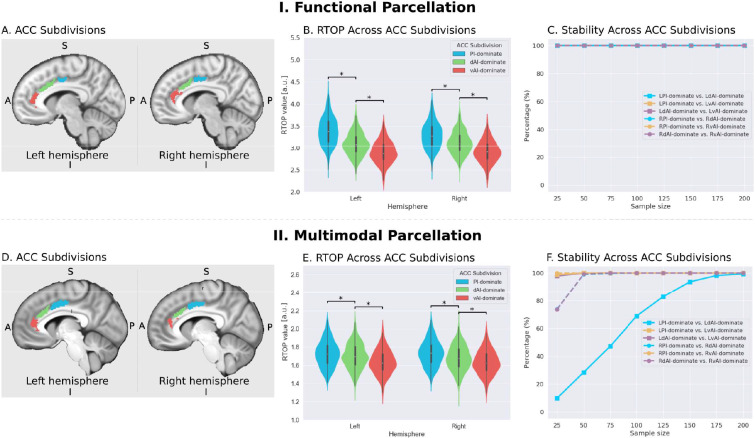
Figure 7. Microstructural properties of anterior cingulate cortex subdivisions mirror profiles in corresponding insula functional subdivisions.
(A) Illustration of ACC subdivisions. Each ACC subdivision preferentially connects to one of the three insular subdivisions defined using an independent functional parcellation (Deen et al., 2011). ACC subdivisions showed significantly greater functional connectivity with one insula subdivision over others (e.g. right PI > right dAI) and (right PI > right vAI) (all ps < 0.01, FDR corrected). (B) RTOP values were significantly different among the three ACC subdivisions in each hemisphere (p<0.001, Bonferroni corrected). The ACC subdivision differentially connected to vAI has smaller RTOP values than the other subdivisions (all ps < 0.001, Bonferroni corrected). (C) RTOP differences among three ACC subdivisions were robust and reliable at sample sizes of N = 25 or more. PI: posterior insula; dAI: dorsal anterior insula; vAI: ventral anterior insula. (D–E) Replication with an independent multimodal parcellation using HCP data (Glasser et al., 2016).