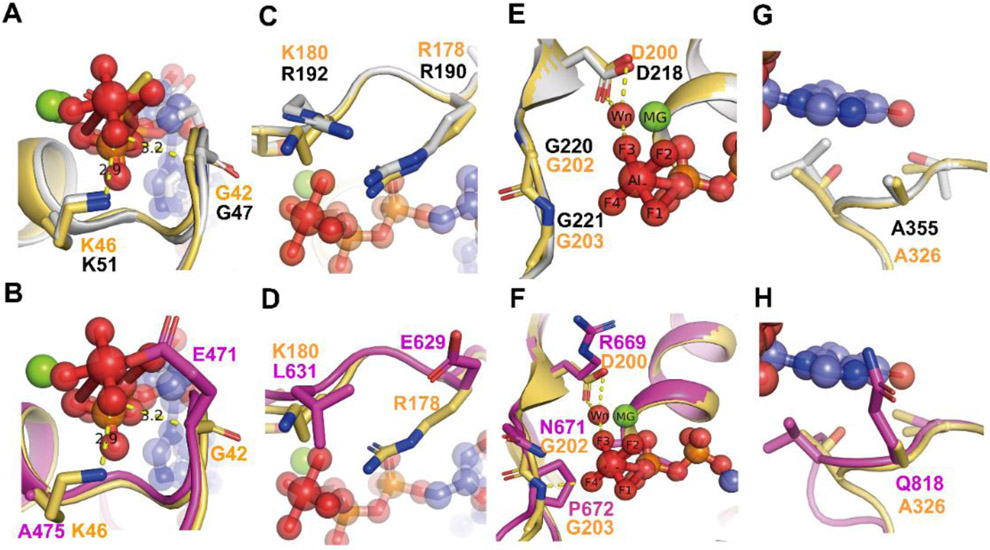
Figure 2. Comparison of the G motifs of AtGPA1 PDB [2XTZ] and the XLG2 G alpha domain model with human Giα1 (PDB [1AGR]).
Grey: AtGPA1, Magenta: XLG2-1 model, Light orange: Giα1. The substrate GDP and AlF4 are shown as sticks and spheres. Mg+2 is shown as green sphere. Wn: nucleophilic water. The main different residues in G1 motif of XLG2 compared with Giα1 and AtGPA1 are shown as sticks (A, B). Both AtGPA1 and Giα1 have the same G and K residues in G1 motif (A). the G42 and K46 in Giα1 were replaced by E471 and Al475 in the counterpart position of XLG2 (B). The main different residues in G2 motif of XLG2 compared with Giα1 and AtGPA1 are shown as sticks (C, D). Both AtGPA1 and Giα1 have the same R residues (known as arginine finger) and similar charged K180 and R192 in G2 motif (C). But in XLG2 no arginine finger exists rather a Glu is at this position. Also, the charged K or R was replaced by a L (D). The main different residues in G3 motif of XLG2 compared with Giα1 and AtGPA1 are shown as sticks E, F. Both AtGPA1 and Giα1 have the same DVGG residues in G3 motif (E). But in XLG2 the DVGG was replaced by R669/N671/P672 relatively (F).The main different residues in G5 motif of XLG2 compared with Giα1 and AtGPA1 are shown as sticks in G and H. Both AtGPA1 and Giα1 have the same A residues in G5 motif (G). While in XLG2 the conserved A was replaced by Q818 (H).