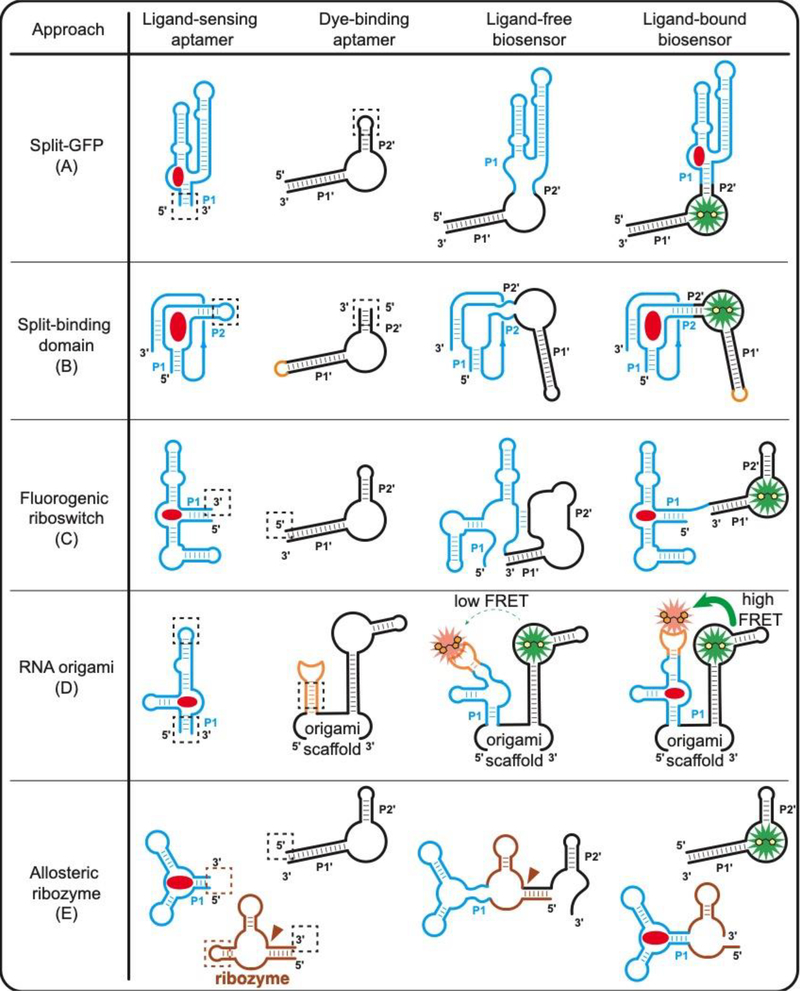
Figure 2.
Design strategies of RNA-based fluorescent biosensors for molecular sensing. Functional RBF biosensors can be generated either by (A) splitting the dye-binding aptamer [16] or (B) splitting the ligand-sensing aptamer [33•]. (C) Fluorogenic riboswitches can be generated by replacing the regulatory expression platform in natural riboswitches with a dye-binding aptamer [34]. (D) Ligand-sensing aptamer can be inserted into an established RNA origami scaffold for ligand-dependent FRET signal change [20•]. (E) Allosteric ribozymes can be fused to a dye-binding aptamer for ligand-dependent release of the fluorogenic aptamer [36]. Red circle, target ligand; dashed square, fusion section between the ligand-sensing domain and the signal reporter domain. Brown triangle, self-cleavage site of ribozyme.