Fig. 2. k-mer matches in real and mock spacers.
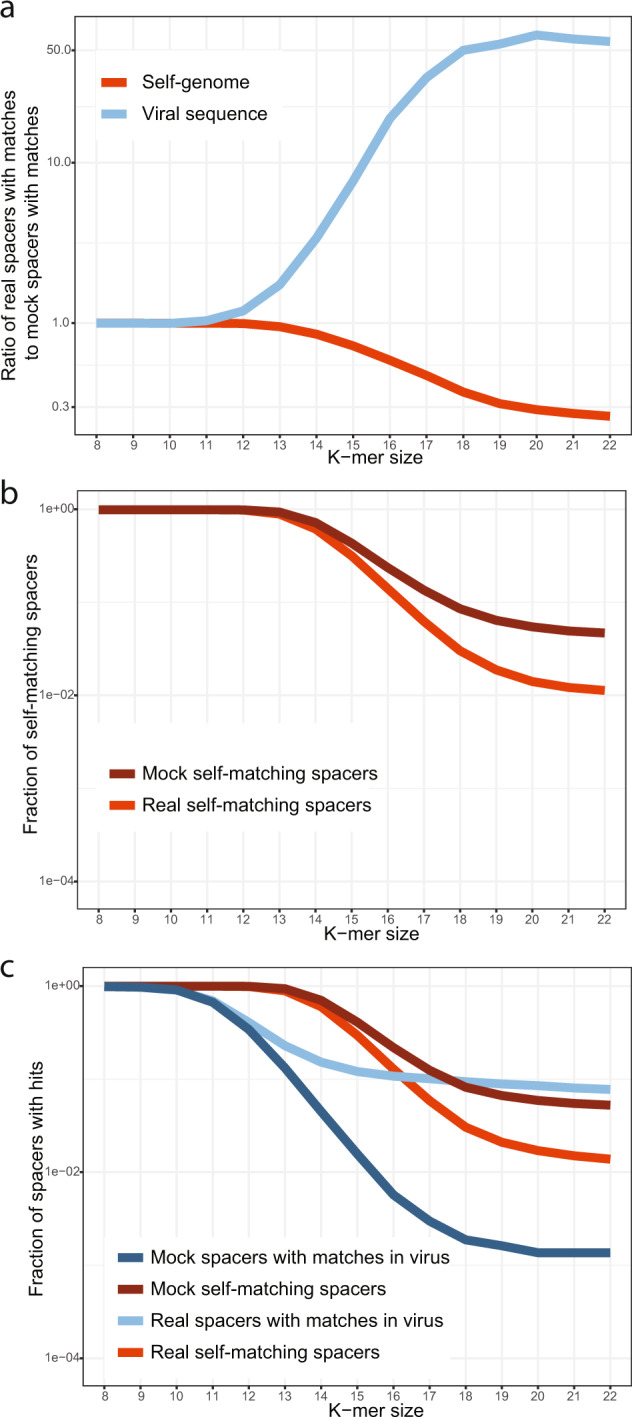
a Ratio of the number of k-mer matches for real spacers to the number of matches for mock spacers: blue, matches in viral genomes, red, matches in host genomes. The results were obtained for the dataset of 154 complete prokaryotic genomes with identifiable protospacers in viral genomes. b Fraction of self-matching spacers (of the total number of spacers) for real (red) and mock (dark red) spacers. The results were obtained for all 2102 complete genomes with CRISPR arrays. c Fractions of virus-matching and self-matching spacers (of the total number of spacers). Blue, real spacers matching viral genomes; dark blue, mock spacers matching viral genomes; red, real spacers matching the host genome; dark red, mock spacers matching the host genome. The results were obtained for the dataset of 154 complete prokaryotic genomes with identifiable protospacers in viral genomes. The underlying data are available at ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/wolf/_suppl/spacers2020/.
