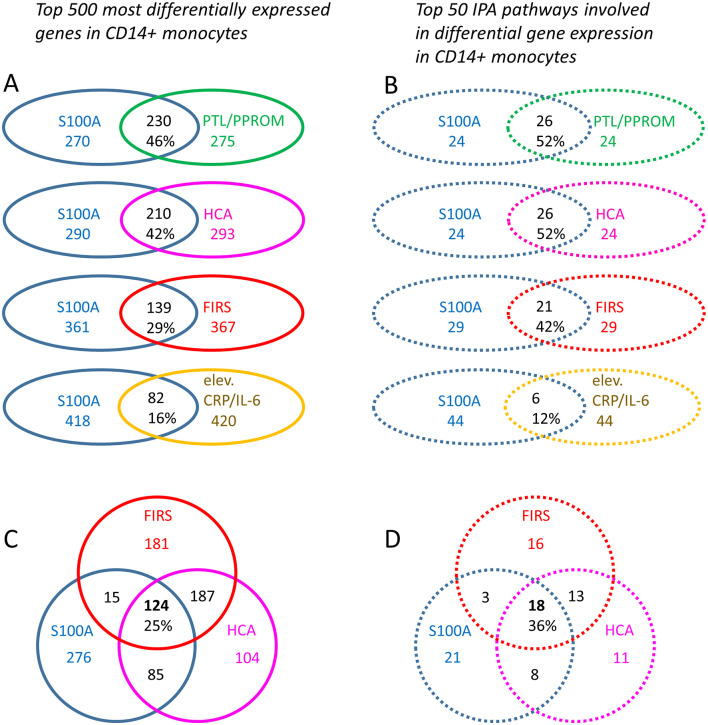
Figure 7.
Differentially expressed monocyte genes and affected IPA pathways common to high monocyte S100A alarmin gene expression and clinical features associated with chorioamnionitis and a fetal inflammatory response in preterm infants. Top 500 differentially expressed (DE) genes (based on p-values) (A) and top 50 affected IPA pathways (B) were identified for each clinical grouping parameter. Common genes and pathways for the S100 high group in relation to HCA and FIRS are shown in (C) and (D), respectively. When statistical significance was identical for the least regulated DE genes, a cut-off of exactly 500 could not be applied and numbers of DE genes may therefore differ slightly between groups. S100A high vs. low gene expression (500 genes, p < 0.0001, blue outline), presence of preterm labor (PTL)/preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM) (505 genes, p < 0.003, green outline); exposure to histological chorioamnionitis (HCA) (503 genes, p < 0.002, violet outline); histological fetal inflammatory response syndrome (FIRS) (502 genes, p < 0.0006, red outline); and elevated CRP/IL-6 in cord blood (506 genes, p < 0.013, yellow outline). The Venn diagrams demonstrate numbers and percentages for overlapping genes and pathways.