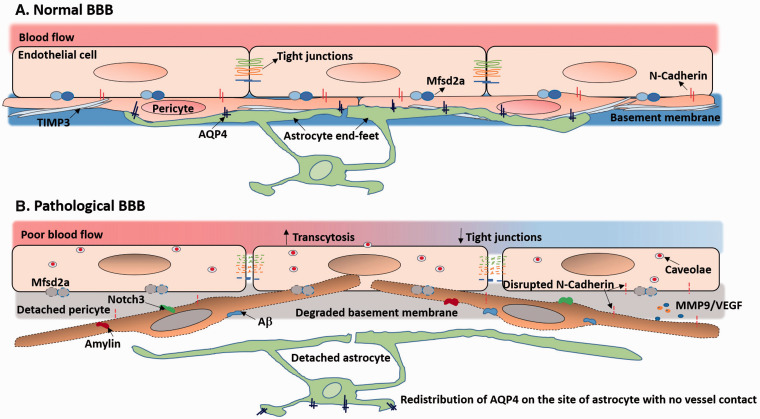
Figure 2.
Role of pericytes in BBB function under normal and pathophysiological conditions: (a) Normally, pericyte coverage enables low transcytosis of ECs and fosters the expression of tight junction proteins and adhesion molecules between pericytes and ECs. Pericytes induce the polarization of astrocytic end-feet that AQP4 anchors at the perivascular site of astrocyte end-feet. Also, pericytes secrete ECM molecules such as TIMP3 to maintain the basement membrane. (b) In diseases, degenerated and migrated pericytes lead to high transcytosis of ECs due to loss of Mfasd2a and disrupted tight junctions. Aβ, amylin, and Notch3 deposition can lead to pericyte dysfunction and loss. Dysfunctional pericytes release MMP9 and VEGF and disrupt N-cadherin to further destabilize the BBB. The basement membrane is degraded as well.