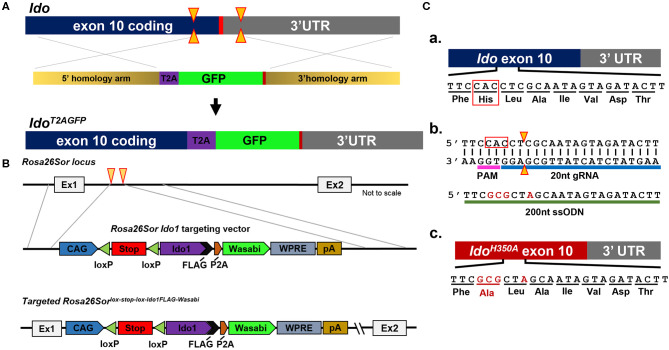
Figure 2.
Schema utilized to generate IDO-targeted transgenic mouse strains. (A) Generation of the Ido1T2AGFP mouse line. CRISPR/Cas9 technology was employed in murine embryonic stem (ES) cells. Two separate guide RNAs directed Cas9 nuclease cleavage of the Ido1 locus, creating double strand DNA breaks (yellow arrow) before and after the stop codon (red bar). The CRISPR ES cell reaction included a plasmid repair template, which encoded the T2A and GFP elements flanked by 5′ and 3′ homology arms of 700nt (tan bars). The T2A and GFP elements were introduced into the endogenous Ido1 locus before the stop codon via homology directed repair (HDR). (B) Introduction of a Cre-dependent Ido1 expression construct into the Rosa26Sor locus by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Two separate guide RNAs directed Cas9 nuclease cleavage at the Rosa26Sor locus, creating double strand DNA breaks (yellow arrows). A plasmid repair temple (Rosa26Sor Ido1 targeting vector) was included in the reaction and introduced via HDR. The edited locus encodes the CAG promoter driven, Cre-dependent conditional expression of a bi-cistronic Ido1 construct. The Ido1 transcript includes a C-terminal FLAG-tag, followed by a P2A element and expression of the Wasabi fluorophore. It also included a WPRE element and the bovine growth hormone polyadenylation (pA) signal. The construct is flanked by 800 bp 5′ and 750 bp 3′ homology arms (gray lines). (C) Generation of the Ido1H350A mouse line. (a) Schematic showing the last coding exon of the Ido1 gene, exon 10. The highlighted region encodes a histidine residue at position 350 (red box) that is essential for mouse IDO enzyme activity; (b) CRISPR/Cas9 technology generated a precise double strand DNA break in the Ido1 exon 10 locus in fertilized mouse embryos (yellow triangle). A 200nt single stranded oligodeoxynucleotide repair template was included in the reaction (green bar). The ssODN introduced point mutations (red letters) into the endogenous Ido1 locus via HDR. These point mutations altered the endogenous coding sequence from CAC→GCG, which changed the amino acid reside from histidine to alanine, H350A (red letters). An additional silent mutation (C→A) was included to add a restriction site for genotype analysis (red letter); (c) Schematic showing the mutated Ido1 exon 10 locus encoding H350A in red.