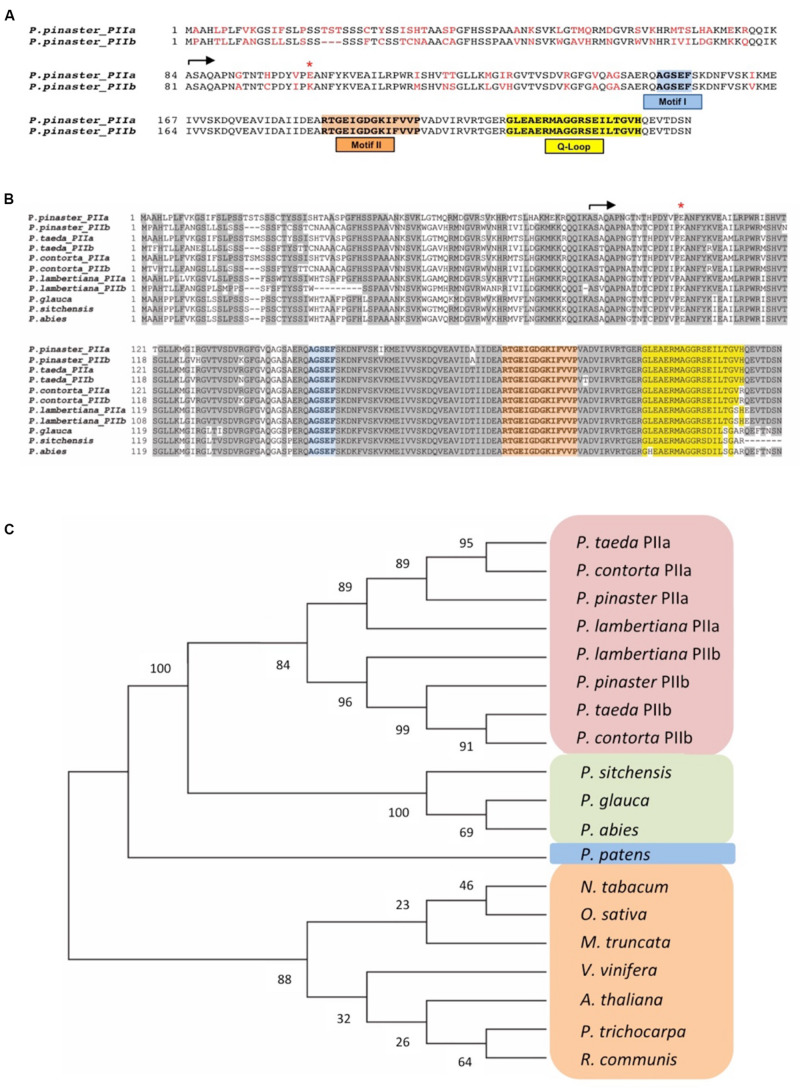
FIGURE 1.
Comparison of PII sequences. (A) Predicted PpPII protein sequences. The conserved sequence motifs (I and II) and the Q Loop position are boxed. The beginning of both mature polypeptides is indicated by an arrow. Residues differing in the two variants are marked in red. The red asterisk highlights a significant amino acid change at position 18 of the mature proteins (see text). (B) Multiple alignments of PII proteins from pine species executed with Clustal X. Conserved sequence motifs in PII proteins are highlighted: in blue Motif I, in orange Motif II, and in yellow the conserved Q-loop of plants. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of PII proteins in angiosperm and gymnosperm species. Alignments were imported into the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analyses (MEGA) software version 7.0 (Kumar et al., 2016). The phylogenetic tree was constructed with the full-length PII amino acid sequences using the neighbor-joining method. Protein sequences were obtained from the following databases: NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), PlantGDB (www.plantgdb.org), TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org), SustainPineDB v.3.0 (http://www.scbi.uma.es/sustainpinedb/sessions/new), and PLAZA (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/plaza/versions/gymno-plaza).