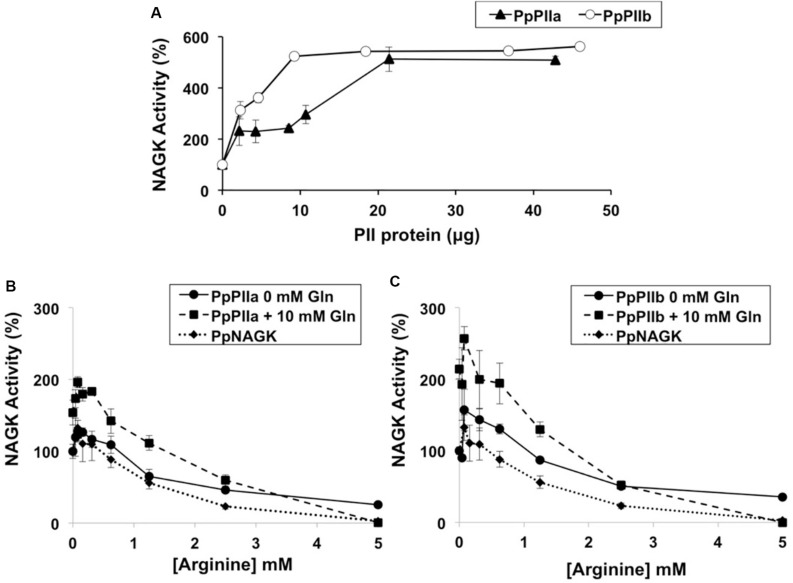
FIGURE 5.
Effects of PpPIIa and PpPIIb on the PpNAGK activity. (A) Effect of increasing amount of PpPIIa (black triangles) and PpPIIb (open circles) proteins on PpNAGK activity. The indicated amounts of PpPII were mixed with 0.65 μg PpNAGK, and the mixtures were placed at 4°C for 10 min to allow complex formation. The reaction was initiated by the addition of the reaction mixture into the PpNAGK-PpPII complex mixture. The N-acetylglutamylhydroxamate assay was used. (B) PpNAGK–PpPIIa complex activity inhibition by arginine with or without added glutamine. (C) PpNAGK–PpPIIb complex activity inhibition by arginine with or without added glutamine. Glutamine 10 mM (black squares); glutamine 0 mM (black circles). PpNAGK activity inhibition by arginine is also shown (black triangles). To test the effect of arginine on the PpNAGK–PpPII complexes, PpPII was first added into the diluted PpNAGK solution, and the two proteins were placed at 4°C for 10 min to allow complex formation followed by the addition of arginine. The arginine effect was also tested in combination with 10 mM glutamine as described above. The continuous spectrophotometric assay was used. Values are the mean ± SD of three independent determinations. NAGK activities (100%) were (A) 108.80 ± 14.35, (B) 726.15 ± 71.58, and (C) 563.17 ± 29.68 nkatal/mg protein. The reaction mixtures contained (A) 0.65, (B) 0.35, and (C) 0.35 μg of PpNAGK protein. The observed increase of PpNAGK activity with PpPIIa and PpPIIb was significant by t-test with a P < 0.1 and enhanced in presence of glutamine with a P < 0.05. Arginine inhibition was significantly relieved by adding glutamine (P < 0.01) in both PpNAGK–PpPII complexes. Each reaction mixture contained 0.35 μg of PpNAGK protein and 0.7 μg of PpPIIa and 0.7 μg PpPIIb.