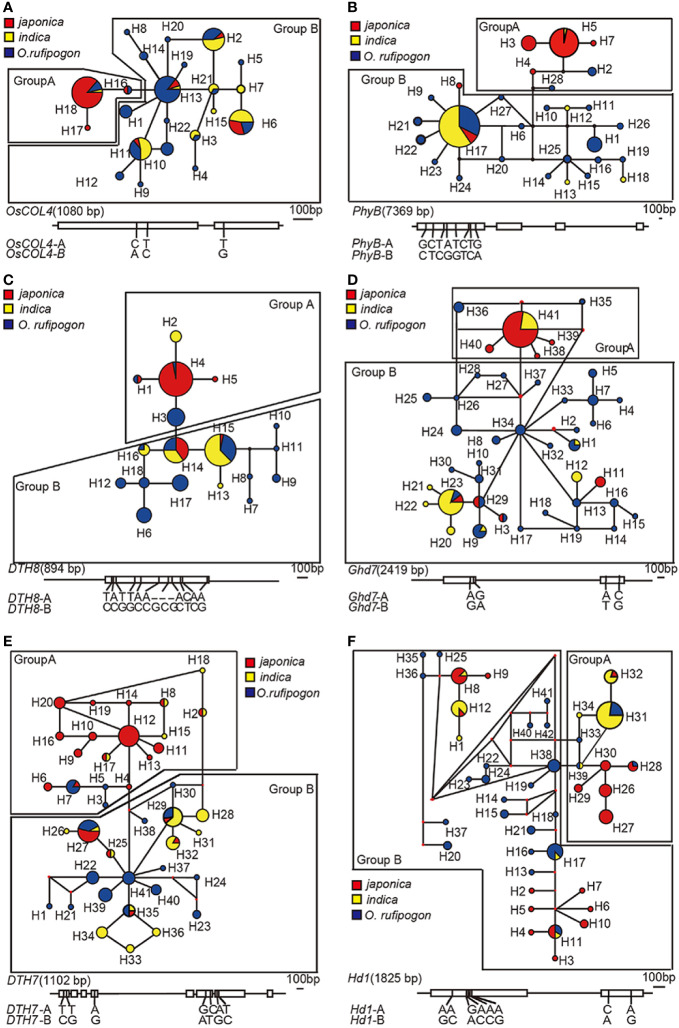
Figure 1.
Network trees of six long-day suppressor genes in cultivated rice. (A) OsCOL4: H_2, H_6, H_11, H_13, and H_18 are high-frequency haplotypes of OsCOL4. (B) PhyB: H_5 and H_17 are high-frequency haplotypes of PhyB. (C) DTH8: H_3, H_4, H_6, H_14, H_15, and H_17 are high-frequency haplotypes of DTH8. (D) Ghd7: H_23 and H_41 are high-frequency haplotypes of Ghd7. (E) DTH7: H_7, H_12, H_27, H_29, and H_32 are high-frequency haplotypes of DTH7. (F) Hd1: H_8, Hap_11, H_12, H_17, H_27 and H_31 are high-frequency haplotypes of Hd1. The size of the circle in each gene's network tree represents the haplotype frequency. Yellow and red represent the two subcultivars of cultivated rice, indica and japonica, and blue represents O.rufipogon. Each gene's network tree corresponds to the SNP on the diagram of long-day suppressor genes below, which illustrates the haplotype-specific SNPs between group A and group B of the long-day suppressor genes.