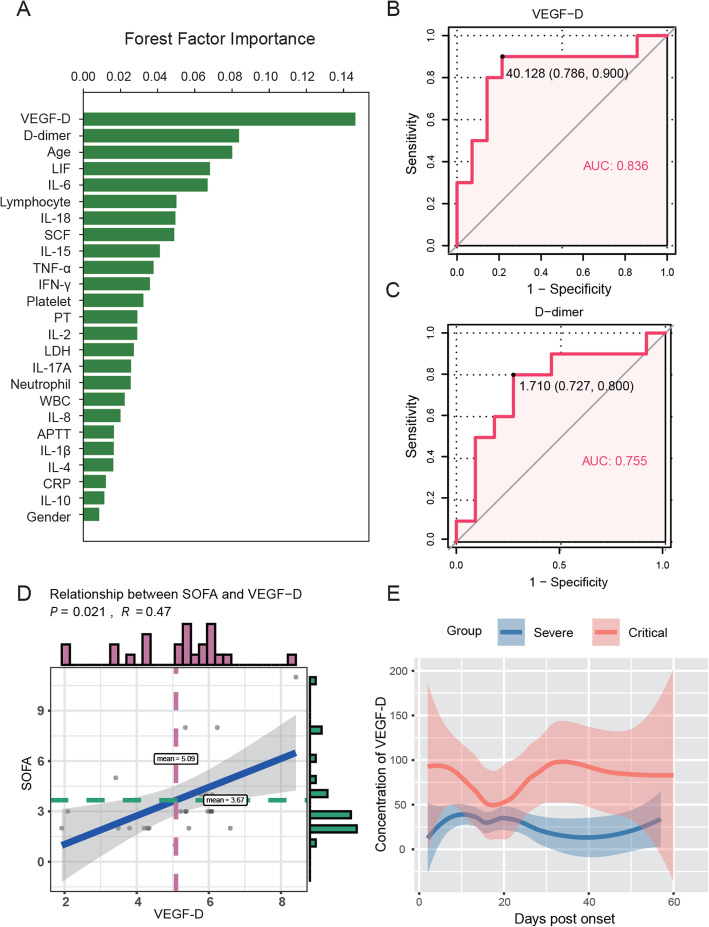
Fig. 1.
A high level of VEGF-D predicted progression of COVID-19. a Eleven clinical indicators and 14 cytokines were considered for inclusion and ranked by importance using random forest. b, c Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses for VEGF-D (b) and d-dimer (c) in COVID-19 patients. d Relationship between VEGF-D and SOFA scores in severe and critical COVID-19 patients was analyzed by the Spearman rank correlation test. e Temporal changes of VEGF-D levels in each group during hospitalization. The median values of each time point (the day from onset) were shown. The 95% interval was plotted as a colored shadow