Central Illustration:
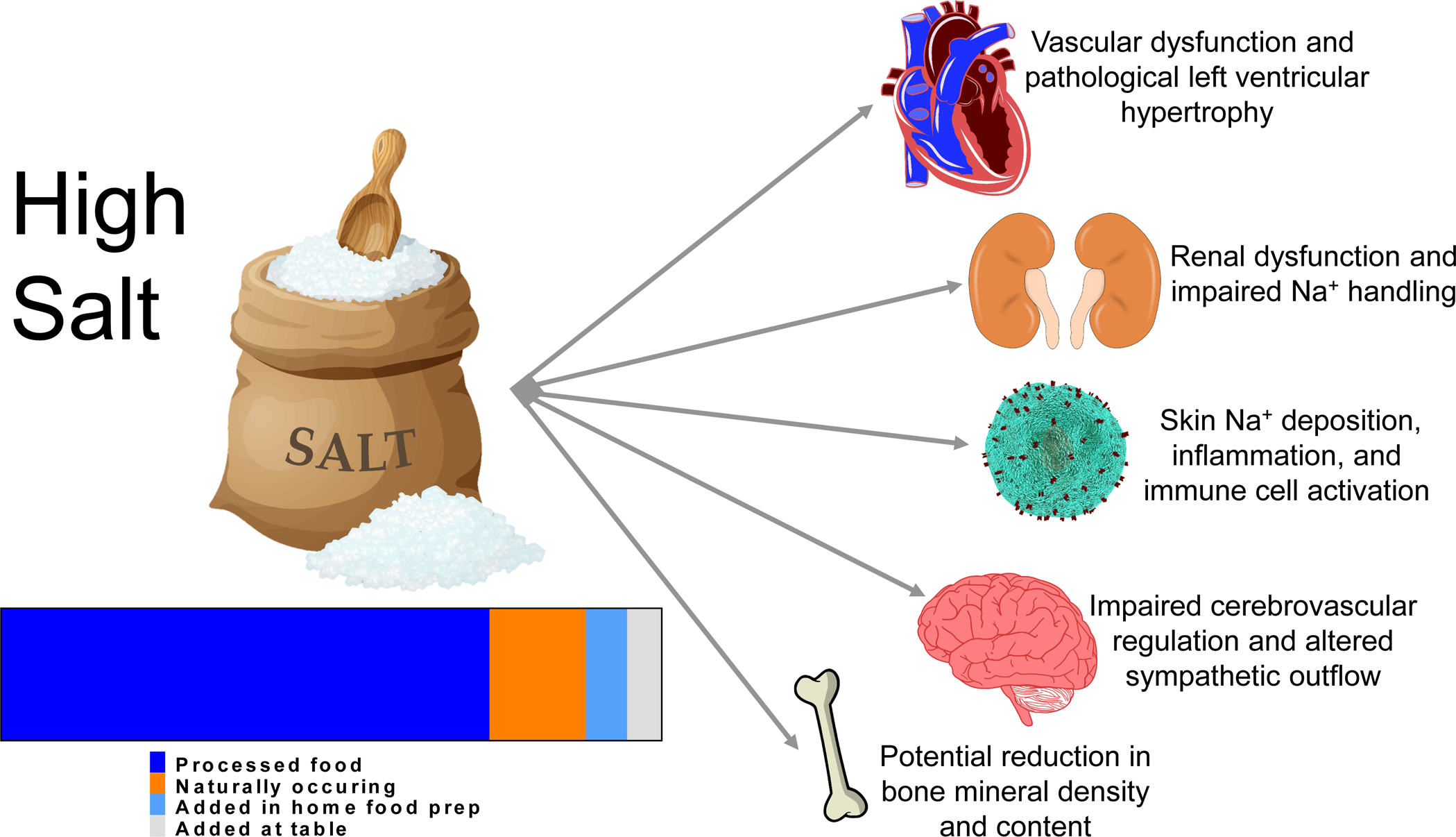
There is agreement that salt diets contribute to high blood pressure and end organ damage. One of the reasons that consumers have had such a hard time reducing sodium intake is that a majority of the sodium consumed in the diet (>70%) comes from processed food followed by naturally occurring sodium, and finally what is added in the home. To the right, the various end organ damage associated with high dietary sodium is depicted. The source of the information on sources of dietary sodium is Harnack et al., 2017. (113).
