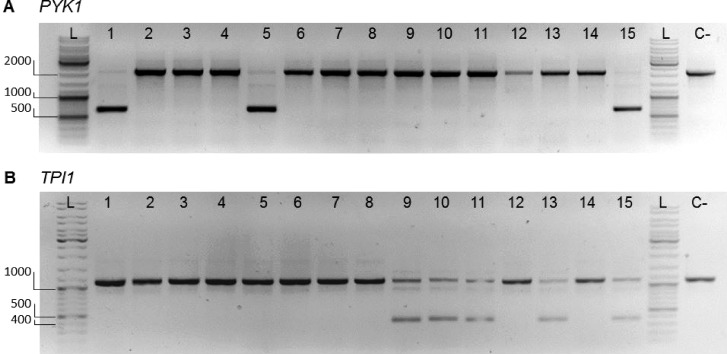
Figure 7.
Diagnostic PCR for selective editing of native glycolytic genes. Separation of PCR products resulting from outside–outside amplification to identify edited (nonwatermarked) and nonedited (watermarked) loci for PYK1 (A) and TPI1 (B) from transformants of IMX1717 (double SinLoG). (A) Lanes 1–15 show the PCR results of amplification of the PYK1 locus of randomly picked colonies. Successful editing of the locus results in a DNA fragment with a length of 670 bp. No editing of the locus results in a DNA fragment with a length of 2177 bp. Primers 11915 and 4667 were used. Lanes 1, 5, and 15 display bands of both sizes revealing selective editing. (B) Lane 1–15 show the PCR results of amplification of the TPI1 locus of randomly picked colonies. Successful editing of the locus results in a DNA fragment with a length of 378 bp. No editing of the locus results in a DNA fragment with a length of 1125 bp. Primers 3514 and 6406 were used. Lanes 9–11, 13, and 15 display bands of both sizes revealing selective editing. A negative control is indicated with “C-“ (IMX1338, SinLog). In the lanes indicated with “L”, GeneRuler DNA ladder mix was loaded. 1% (w/v) agarose in TAE.