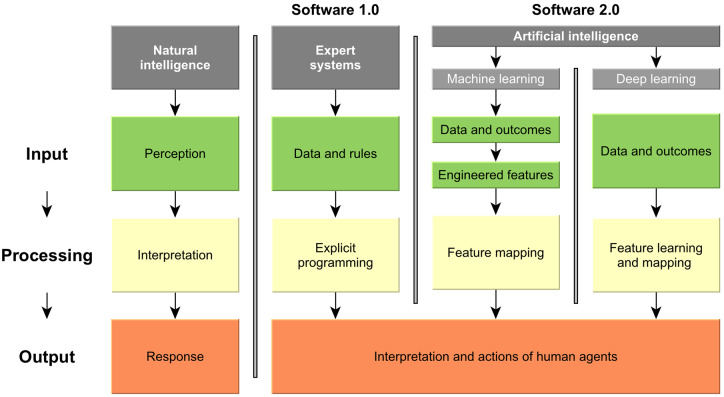
Figure 1.
Natural and computer intelligence. Natural intelligence is characterized by perception, interpretation and biological response. In contrast, computer intelligence does so far not replace human responses, but largely supports human interpretation and action. Traditional software (1.0) as one pillar of computer intelligence is supported by rules-based expert systems; they take data and explicitly programmed logical rules to generate narrow, specialized outcomes, thereby outperforming humans in these tasks. Software 2.0 instead uses data and outcomes to infer the rules: In classical machine learning, the features are first engineered by human experts and then learned (e.g., regression modeling). In deep learning, relevant features are learned and mapped in one step, without human feature engineering; this allows to leverage even complex data structures like imagery or language. Modified after Kolossváry et al. (2019).