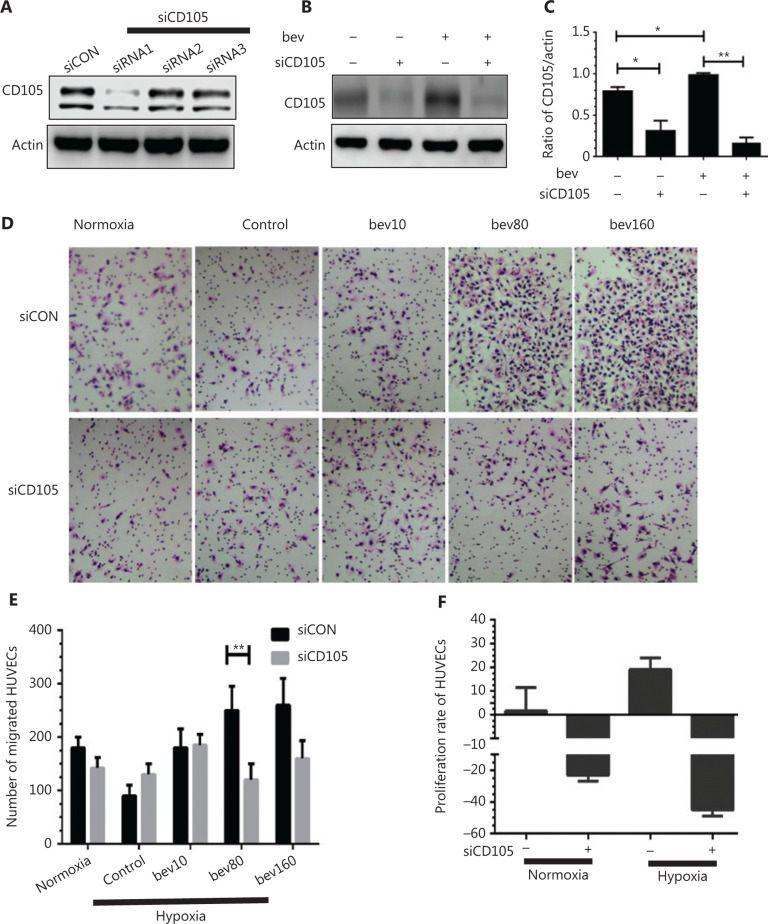
Figure 7.
CD105 siRNA suppresses CD105 expression as well as migration and proliferation of HUVECs promoted by bevacizumab. (A) CD105 protein levels following siCD105 (CD105 siRNA) treatment determined via Western blot. The CD105 siRNA sequences are as follows: siRNA1, 5′-CCA UGA CCC UGG UAC UAA A-3′ and 3′-GGU ACU GGG ACC AUG AUU U-5′; siRNA2, 5′-UGA CCU GUC UGG UUG CAC ATT-3′ and 5′-UGU GCA ACC AGA CAG GUC AGG-3′; siRNA3, 5′-GAG GUG ACA UAU ACC ACU A-3′, 5′-CUC CAC UGU AUA UGG UGA U-3′; and siCON, 5′-UUC UCC GAA CGU GUC ACG UTT-3′ and 5′-ACG UGA CAC GUU CGGAGAATT-3′. CD105 was markedly downregulated by siRNA1, which was selected for subsequent experiments. (B) Western blot assessment of CD105 protein levels following bevacizumab treatment in the presence or absence of siCD105 (CD105 siRNA). (C) Densitometry analysis of CD105 protein levels from B. Data represent mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; Student’s t-test. (D) Typical images of migrated HUVECs in transwell assays following bevacizumab treatment in the presence or absence of CD105 siRNA (siCD105); normoxia: normal oxygen vehicle, control: hypoxia, bevacizumab 0 μg/mL, bev10, bev80, bev160: bevacizumab 10 μg/mL, 80 μg/mL, 160 μg/mL. (E) Number of migrated HUVECs. Data represent mean ± SD, **P < 0.01; Student’s t-test. (F) Proliferation rate of HUVECs decreased following treatment with siRNAs targeting CD105 under both normal and hypoxia conditions. Data represent mean ± SD.