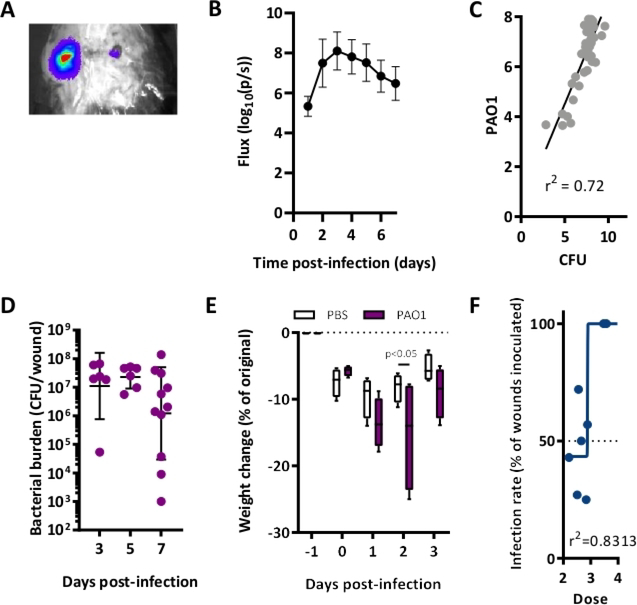
Figure 3: P. aeruginosa wound infection can be detected through 7 days of infection.
(A) Representative image of a mouse infected with PAO1:lux with bioluminescence overlay on excisional wounds. (B) Luminescent signal reflecting wound bacterial burden. N = 6 wounds. Inoculation: 105 CFU/mL PAO1. (C) Linear regression analysis of in vivo luminescent signal and bacterial CFU of PAO1:lux-infected wounds, collected 4–7 days post-inoculation with 105 CFU/mL to allow for a range of bacterial burdens. (D) Bacterial burden in CFU/wound over time in mice infected with 105 CFU/mL PAO1:lux. (E) Weight change (relative to weight before wound excision surgery on T = −1) N = 4 mice/group. Depicted are boxplots for 5–95 percentile. Statistics are Two-way ANOVA corrected with Sidak multiple comparison. (F) Nonlinear regression analysis of wound infection rate used to calculate the IC50 for PAO1 three days post-inoculation. All graphs are representative of n≥3 experiments. This figure has been modified from Sweere et al. 201913.