FIG 2.
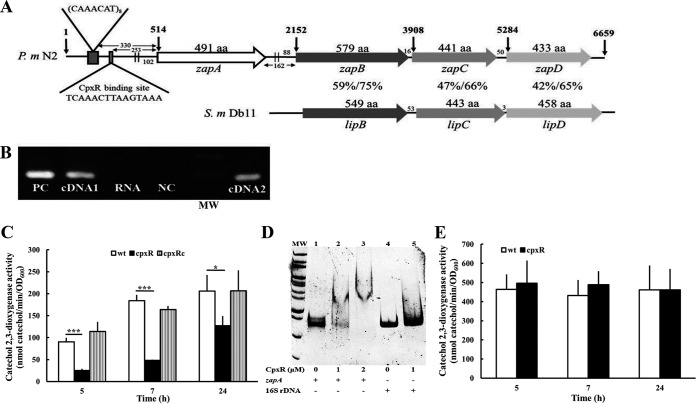
P. mirabilis zapABCD locus and the zapABCD operon regulated by CpxR. (A) Genomic organization of the zapABCD locus in P. mirabilis. Contained within a 6,659-bp region are four open reading frames (ORFs), zapA, zapB, zapC, and zapD. Amino acid numbers are listed on the top of each ORF. The vertical arrow indicates the nucleotide number within this locus. The two parallel lines upstream of zapA and zapB indicate the RpoD binding site. The CpxR binding site and CAAACAT repeat sequence preceding the zapA start codon are indicated. The nucleotide numbers of the intergenic space and the nucleotide distance of the RpoD binding site to the zapA and zapB start codon are also shown. Percent amino acid identity and similarity between P. mirabilis N2 ZapB/C/D and the corresponding LipB/C/D of S. marcescens Db11 by the BLAST analysis are shown. (B) The zapABCD forms an operon. We diluted overnight bacterial cultures and incubated the cultures for another 5 h at 37°C. Total RNA was prepared, and reverse transcription was carried out, with one primer annealing to zapD and the other to zapB. The cDNA product was used to amplify a zapA DNA fragment. For control reactions, RNA without reverse transcriptase (no RT) or genomic DNA was used as the template. The representative result of three independent experiments is shown. PC, genomic DNA as a positive control; cDNA1, cDNA from zapD; RNA, RNA without reverse transcriptase as a negative control; NC, ddH2O negative control; MW, molecular weight (size markers); cDNA2, cDNA from zapB. (C) The zapA promoter activities of the wild-type, cpxR mutant, and cpxRc strains. Bacterial cells with the zapA reporter plasmid were grown overnight, diluted, and incubated for 5, 7, and 24 h at 37°C before the XylE activity was measured as described previously. (D) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of purified P. mirabilis CpxR with the zapA promoter fragment. The DNA fragments (0.1 μg) of the zapA promoter (373 bp) or 16S rRNA gene promoter (380 bp) obtained by PCR were incubated with the indicated concentrations of the CpxR protein. After protein-DNA complex formation, the samples were resolved on a 5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The representative result of three independent experiments is shown. Arrow, protein-DNA complex; lane MW, size markers; lanes 1 to 3, zapA promoter DNA with CpxR; lanes 4 and 5, 16S rRNA gene promoter DNA with CpxR. (E) The zapB promoter activities of wild-type and cpxR mutant strains were determined as described in panel C. (C and E) The data are the averages and standard deviations of the results from three independent experiments. Significant differences were determined by using Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). wt, wild type; cpxR, cpxR mutant; cpxRc, cpxR-complemented strain.