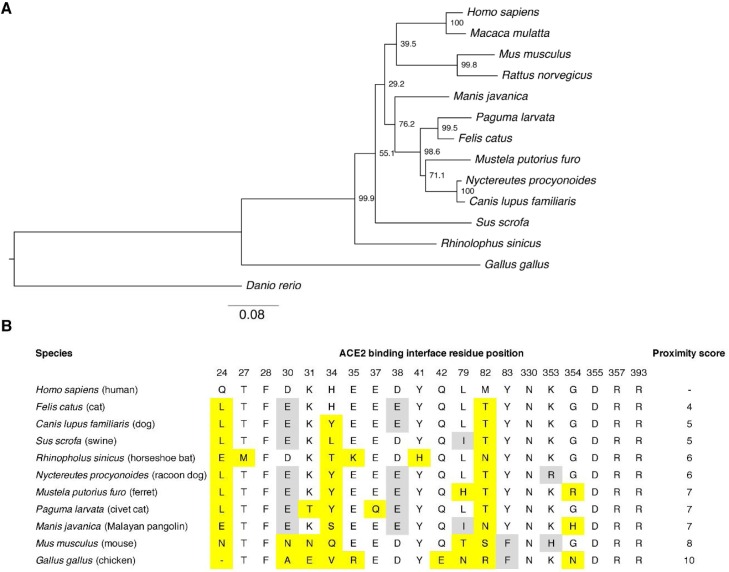
Fig. 2.
Comparative analysis of ACE2 in different mammalian species. A. Phylogenetic tree of ACE2 sequences from different species. The ACE2 sequences from various animal species were aligned using MUSCLE and a maximum-likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree was generated using MEGAX. Bootstrap values shown at nodes were calculated from 1000 replicates. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. B. Comparative analysis of ACE2 amino acid composition at residue positions involved in the ACE2-virus binding interface. The ACE2 sequences of ACE2 from selected species were aligned and the amino acid found at each of the residue positions involved in the binding interface are shown. Yellow highlight indicates a substituted residue compared to the human ACE2 sequence. A grey highlight indicates a conservative change in residue composition compared to human ACE2 sequence. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).