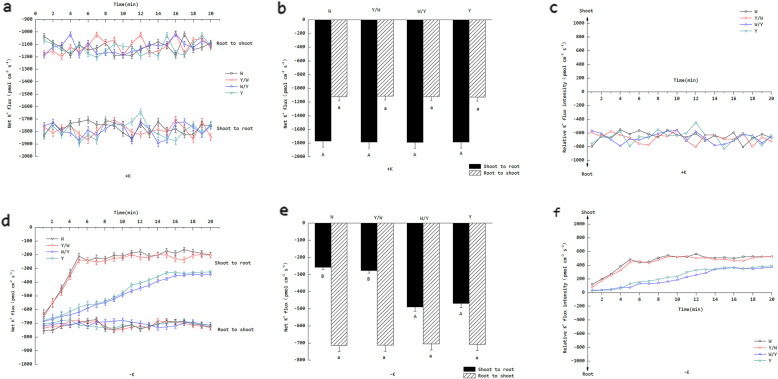
Fig. 3.
Effects of grafting on the net K+ flux in tobacco hypocotyls. The tobacco graft combinations included the nongrafted tobacco W (Wufeng No.2) and Y (Yunyan 87) and grafted tobacco Y/W (Y grafted onto W) and W/Y (W grafted onto Y). a The net K+ flux dynamics of the hypocotyls under normal K levels (5 mmol L− 1) over 20 min. The net K+ flux at transverse sections of the shoot constituted the downward ion current of the phloem, which was defined as “Shoot to root,” while the net K+ flux at transverse sections of the root constituted the upward ion current of the xylem, which was defined as “Root to shoot.” For all ion flux measurements, the sign convention is “influx positive.” (b) The mean net K+ flux of the hypocotyls under normal K levels (5 mmol L− 1) over 20 min. Different uppercase and lowercase letters denote significant differences (P < 0.05) between each grafting combination. (c) The relative K+ flux under normal K levels (5 mmol L− 1). The relative K+ flux is calculated by subtracting the downward ion current from the upward ion current. The numerical quadrant represents the direction of the relative flux of K+. (d) The net K+ flux dynamics of the hypocotyls under K starvation (0.5 mmol L− 1) over 20 min. (e) The mean net K+ flux of the hypocotyls under K starvation (0.5 mmol L− 1) over 20 min. (f) The relative K+ flux under K starvation (0.5 mmol L− 1)