Fig. 4.
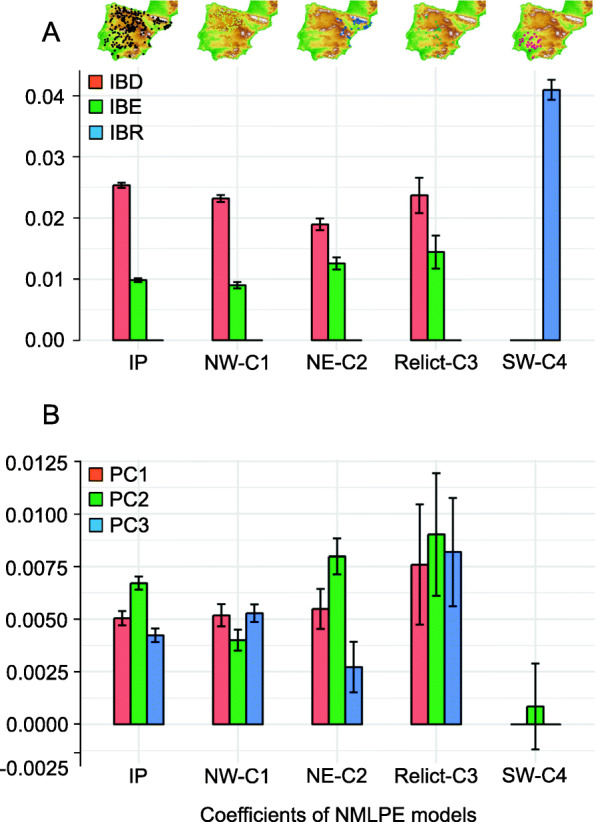
Effects of isolation-by-distance (IBD), isolation-by-environment (IBE) and isolation-by-resistance (IBR) on genetic differentiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. a Coefficients (± SD) of the top-ranked nested maximum-likelihood population effects models (NMLPE) testing the effect of IBD, IBE and IBR on genetic differentiation in A. thaliana. b Model averaged coefficients (± SD) for three Principal Component (PC) axes accounting for more than 75% of the total variance. Model averaging was conducted using the subsample of models exhibiting ∆AIC < 2 regarding the top-ranked model, if more than one. In all cases, model estimates for the analysis conducted for the entire Iberian Peninsula (IP) and the four genetic clusters (NW-C1, NE-C2, relict-C3, and SW-C4) are shown. Maps with the geographic distribution of populations used in each analysis are also given. Maps were obtained from the National Center for Geographic Information (CNIG) of Spain
