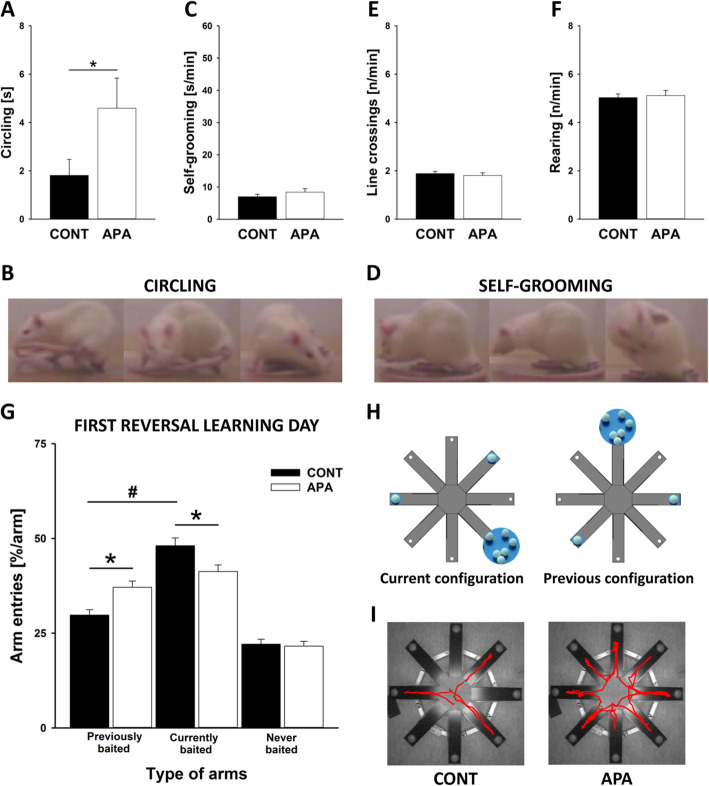
Fig. 4.
Repetitive and stereotyped patterns of behavior in APA rats. a Time spent circling [s] during tail-chasing. b Exemplary image of circling behavior. c Time spent self-grooming [s/min]. d Exemplary image of self-grooming behavior. e Frequency of line crossings [n/min]. f Frequency of rearing behavior [n/min]. g Repetitive and stereotyped behavior was also tested using a radial eight arm maze with three consistently baited arms. After this spatial learning period, subjects were tested for reversal learning and the positions of baited arms were changed. Arm entries [%/arm] in previously, currently, and never baited arms during all four sessions of the first reversal learning day were counted. h Schematic illustration of the different spatial learning and reversal learning configurations (termed previous and current configuration, respectively). i Exemplary tracking profiles of a single rat during the fourth trial of the first reversal learning day, measured by using the automated video tracking software EthoVision (Noldus Information Technology, Wageningen, The Netherlands), with tracking profiles shown in red. *p < .05; #p < .05