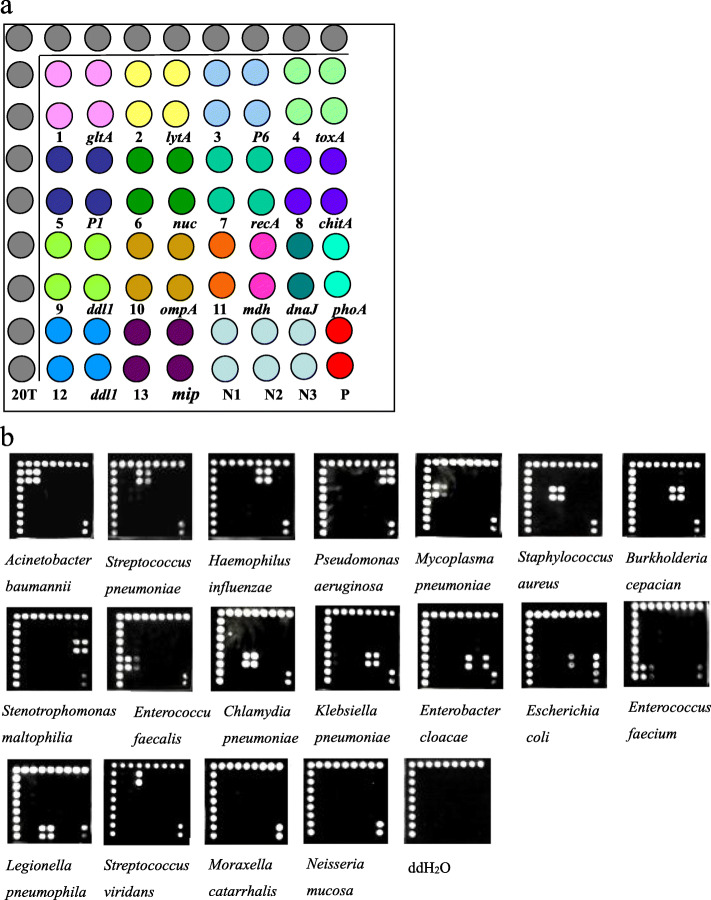
Fig. 1.
a. The layout of the hybridization capture-chip. The probe 20 T is the QC probe. The probe N1, N2, N3 are the negative control probes. The probe P is the universal 16S rDNA probe. Each probe was spotted as two. The sequences of probe 1–13 all come from 16S rDNA and their corresponding target pathogen were: 1 Acinetobacter baumannii; 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae; 3 Haemophilus influenzae; 4 Pseudomonas aeruginosa; 5 Mycoplasma pneumoniae; 6 Staphylococcus aureus; 7 Burkholderia cepacia; 8 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; 9 Enterococcus faecalis; 10 Chlamydia pneumoniae; 11 Klebsiella pneumoniae or Enterobacter cloacae or Escherichia coli; 12 Enterococcus faecium; 13 Legionella pneumophila, respectively. b. The typical hybridization results of fifteen species of bacterial pathogens in pneumonia, non-target bacteria from pure bacterial cultures and ddH2O