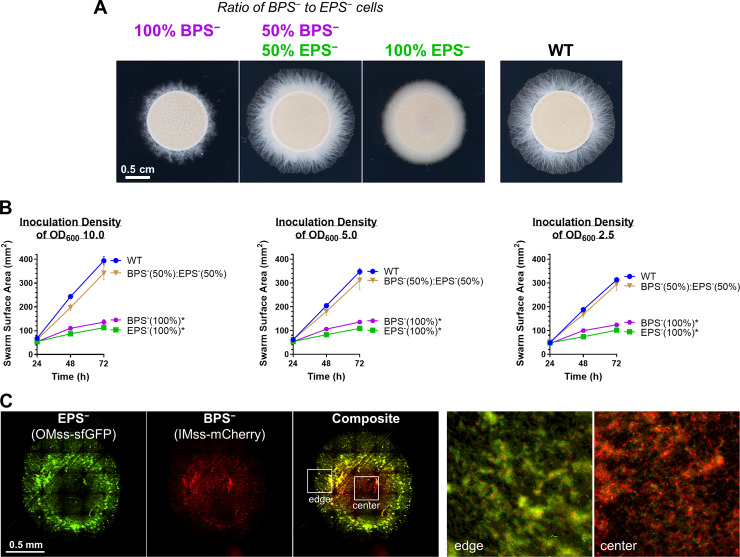
Fig 5. Cross-complementation of EPS versus BPS deficiencies via strain mixing.
(A) EPS− (ΔwzaX) and BPS− (ΔwzaB) cells from exponentially growing cultures were mixed at the indicated ratios to a final concentration of OD600 5.0. Pure and mixed cultures were then spotted on CYE 0.5% agar and imaged after 48 hours at 32°C. (B) Swarm areas with temporal tracking of pure and mixed cultures were treated as described and imaged at 24, 48, and 72 hours. Each data point is the average of 4 biological replicates and is displayed +/− SEM. Mixed/pure cultures with statistically significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in mean surface areas (at 72 hours relative to WT) are indicated with an asterisk (*), as determined via 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Raw values and detailed statistical analysis are available (S1 Data). (C) EPS− (ΔwzaX) PpilA-OMss-sfGFP and BPS− (ΔwzaB) PpilA-IMss-mCherry cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio as in (A), spotted on agar pads, and imaged via fluorescence microscopy after 24 hours. The 2 images on the right are magnified views of the colony center and colony edge approximately indicated by the inset boxes in the “composite” image. BPS, biosurfactant polysaccharide; CYE, casitone-yeast extract; IMss, inner-membrane signal sequence; OMss, outer membrane signal sequence; OD600, optical density at 600 nm; sfGFP, superfolder green fluorescent protein; WT, wild type.