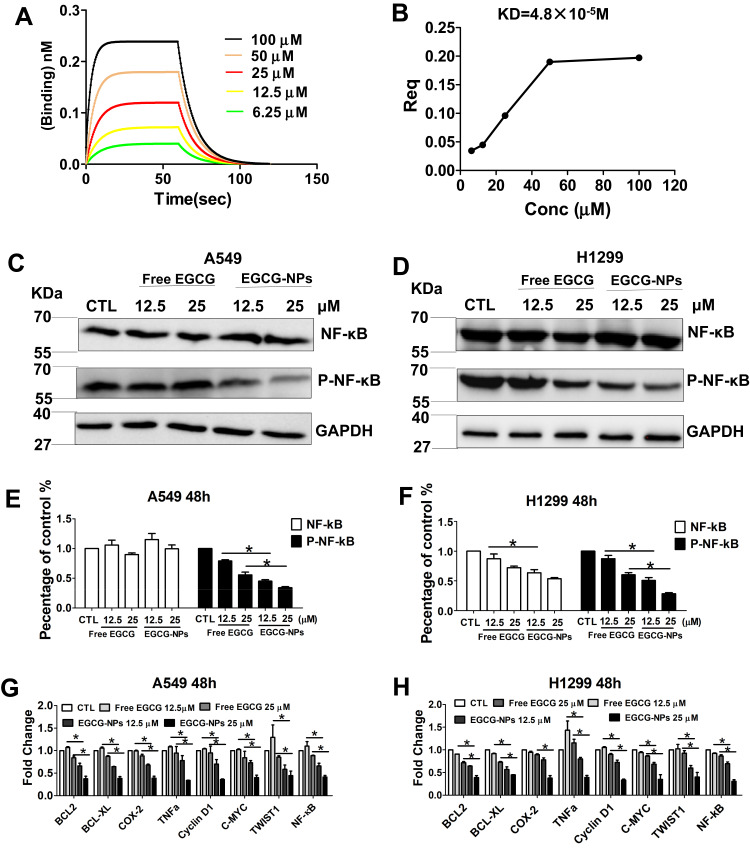
Figure 5.
EGCG-NPs induce lung cancer apoptosis via NF-κB inhibition. (A, B) NF-κB specifically binds to the active form of EGCG by BLI kinetic binding assay. Biotin-labeled NF-κB was immobilized onto the Streptavidin Biosensors and tested for kinetic binding to various concentrations of EGCG. The dissociation constant of NF-κB and EGCG is 4.8×10−5 M. (B) Steady-state analysis, R2=1. (C–F) Western blot analysis of total NF-κB and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 in A549 and H1299 whole-cell lysates after treatment with EGCG and EGCG-NPs (12.5 μM and 25 μM) for 48 h. (G, H) qRT-PCR analysis of C-MYC, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, COX-2, TNF-α, TWIST1, and MMP2 after treatment with EGCG and EGCG-NPs (12.5 μM and 25 μM) for 48 h. Data are shown as the mean ±SDs. (n=3). * P < 0.05.