Figure 2.
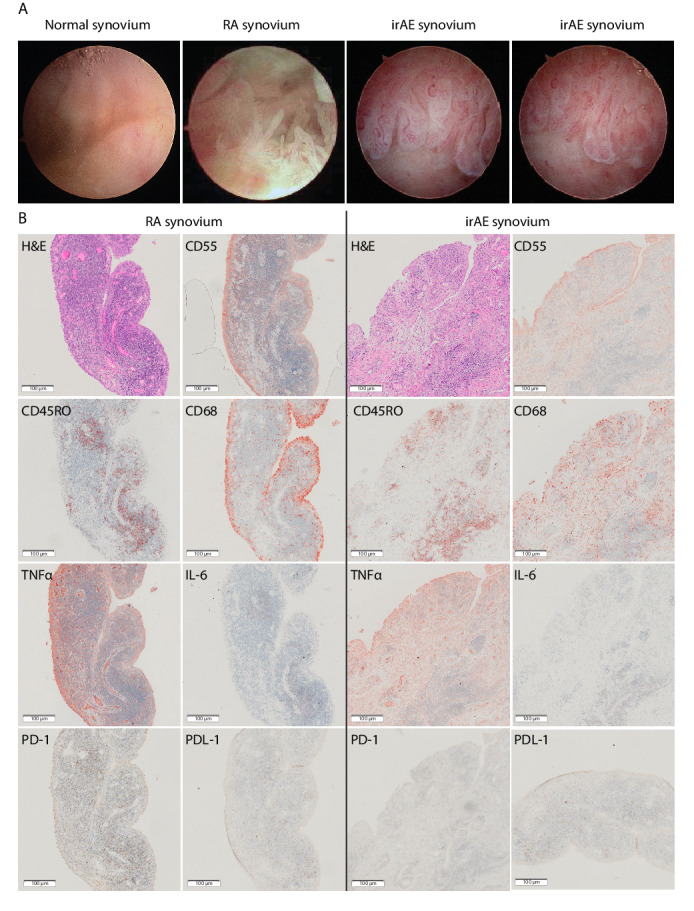
Rheumatic irAE recapitulates features of rheumatoid arthritis synovitis. (A) Camera-guided arthroscopic images show extensive hypervascularization and synovial hyperplasia in both irAE and early RA compared with the normal synovium. (B) Immunohistochemistry on synovial tissue sections (rheumatic irAE; left, RA; right) stained with: H&E; CD55 highlighting synovial membrane lining fibroblasts; CD68 identifying diffuse infiltration of macrophages in irAE compared with subsynovial lining localization in RA; CD45RO identifying abundant memory T cell infiltration; TNFα and IL-6 labeling showing differential proinflammatory cytokine expression in both samples; PD-1 demonstrating absent labeling in irAE compared with RA; and PDL-1 positive labeling in both irAE and RA. Single labeled slides were counter stained with Haematoxylin. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue section images are representative of all 3 RA patients. All images were captured at ×20 magnification. IL-6, interleukin-6; irAE, immune-related adverse-events; PD-1, programmed cell death protein-1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor α.
