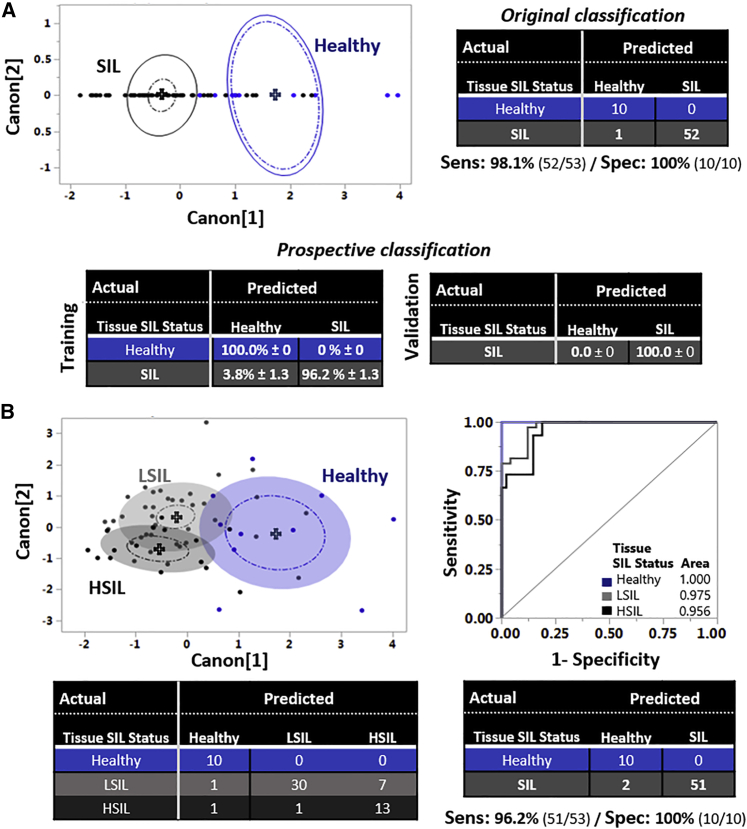
Figure 5.
Automated Tissue Classification Using Optically Derived Morphofunctional Tissue Metrics
(A) 2D canonical QDA scatterplot showing the tissue separation of the healthy (blue; N = 4 participants; 10 tissue stacks) and SIL (black; N = 21 participants; 53 tissue stacks) tissue stacks. Each point represents 1 tissue stack. Full-line ellipses represent 50% of data coverage, crosses display group means, and dashed ellipses indicate 95% confidence intervals for the mean of each tissue group, respectively. Original classification outcomes are presented based on the comparison of the QDA model predictions for the healthy (blue) and SIL (black) groups. Mean prospective classification outcomes from 3 randomized runs are shown for the training and validation sets based on the comparison of the QDA model predictions for the healthy and SIL groups.
(B) Left: 2D canonical QDA scatterplot showing in space the tissue separation of the healthy, LSIL, and HSIL tissue stacks. Colored ellipsoids represent 50% of data coverage. Right: ROC analysis of the QDA discrimination model at the healthy (blue), LSIL (light gray), and HSIL (dark gray) levels. AUC for each tissue group is also shown, indicating discrimination accuracy. Bottom: original classification outcomes based on the comparison of the QDA model predictions at the healthy (blue), LSIL (light gray), and HSIL (dark gray) levels and merged classification outcomes at the healthy (blue) and SIL (gray) levels, with corresponding histopathological evaluations and extracted sensitivity and specificity outcomes.