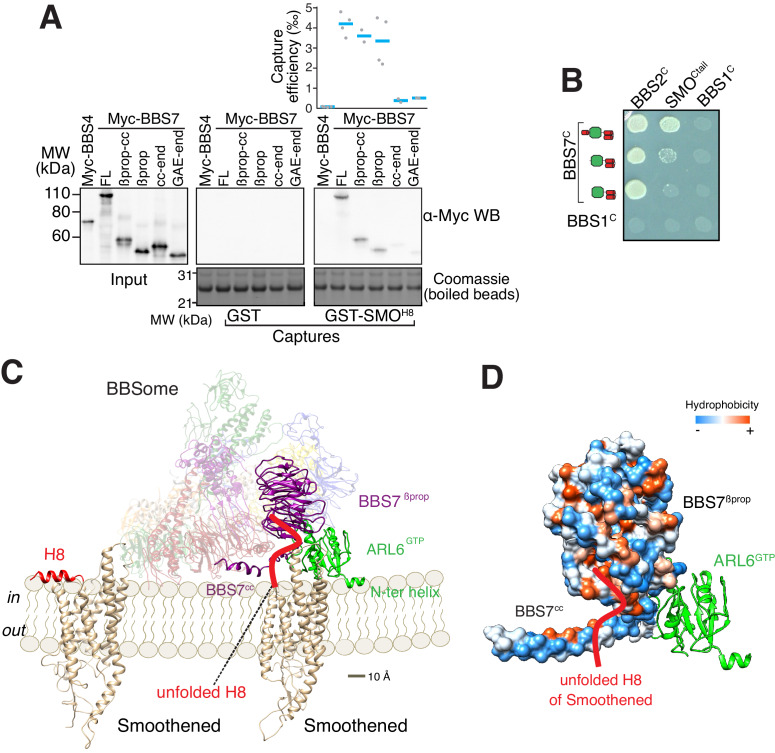
Figure 5. A model for binding of the BBSome to membranes and cargo.
(A) Capture assays of BBS7 find that BBS7βprop engages SMOH8. The boundaries of each truncation are βprop, aa 1–332; βprop-cc, aa 1–378; cc-end, aa 326–672; and GAE-end, aa 375–672. Results are presented as in Figure 3. (B) YTH assays show that the deletion of BBS7cc impairs the interaction of BBS7C with SMOCtail (top row), but not with a C-terminal fragment of BBS2 (BBS2C, residues 324–712) (middle rows). BBS1C serves as non-interacting control. Growth controls on diploid-selective medium are shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1A. (C) Diagram illustrating the proposed interaction of SMO with the membrane-bound BBSome–ARL6GTP complex. For clarity, ARL6GTP and the BBS7 domains involved in SMO binding (BBS7βprop and BBS7cc) are shown in solid colors with the remaining subunits shown with reduced opacity. Helix 8 (H8) of SMO is folded in the absence of partners, and is proposed to become a random coil in the SMO–BBSome complex. (D) Hydrophobicity surface of the BBS7βprop and BBS7cc domains, showing a plausible binding cleft for unfolded SMOH8 (shown in red). ARL6GTP is shown in ribbon representation.