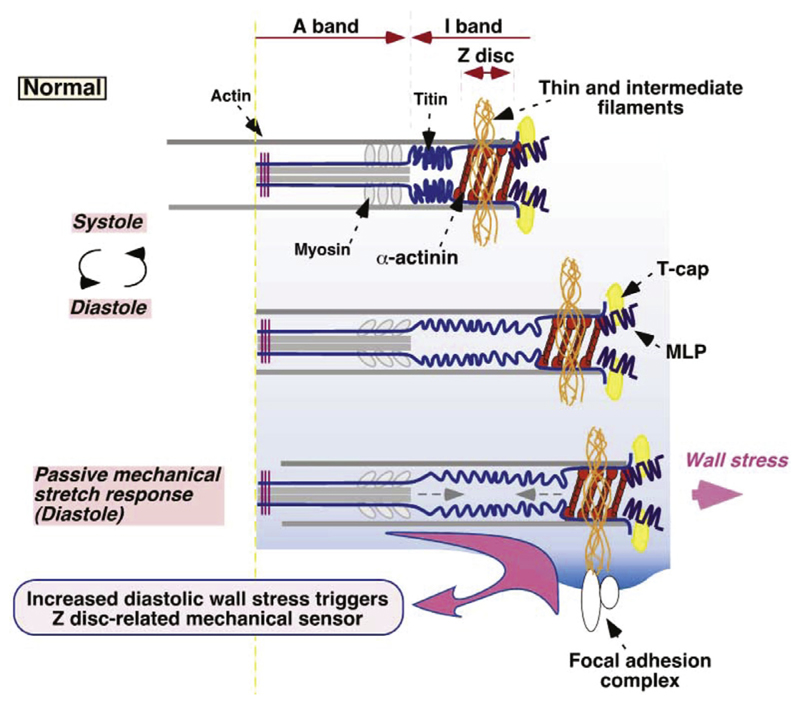
Fig. 9.
A schematic showing the interaction between thin and intermediate filaments within the titin/Z-disc complex with focal adhesion complexes, hence serving as mechanosensors. Titin has elastic sequences in the I-band, serving as springs saving elastic energy during diastole and relasing it to regain the initial sarcomere length at systole. At peak diastole the titin elastic segments uncoil and add their contribution to ventricular wall distensibility. Increased stretch of the titin elastic segments is sensed and activates downstream signals for cardiac remodeling. Adapted with permission from [168].