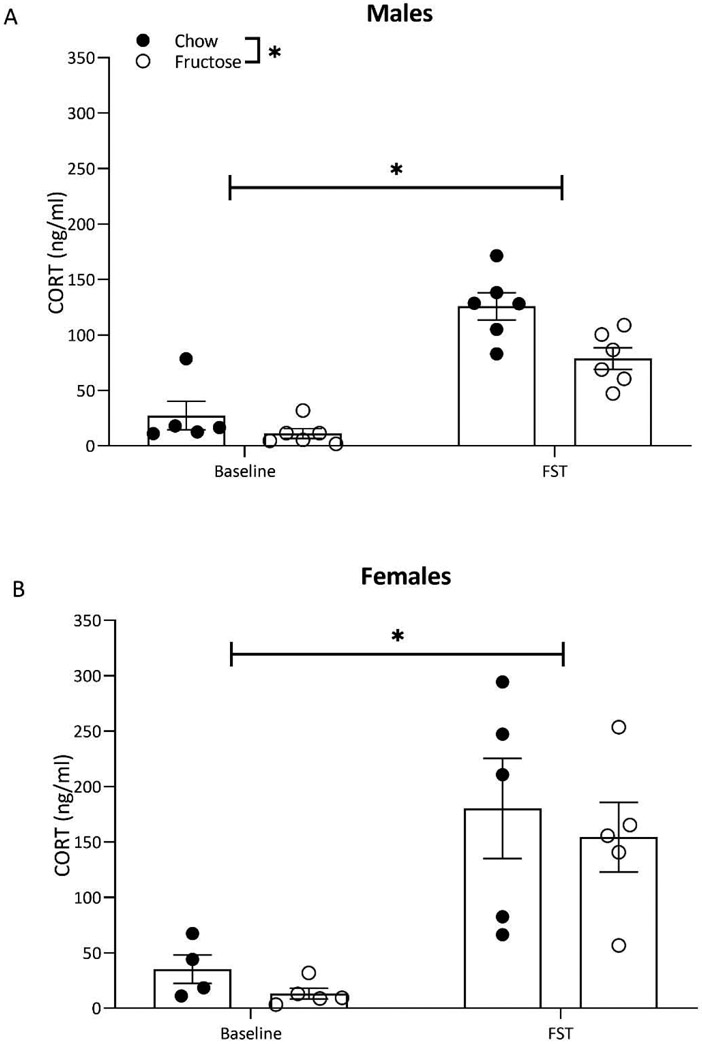
Figure 4:
Exposure to acute stress in the form of a 10-minute forced swim test increased blood corticosterone in both sexes based on within sex two-way ANOVA (diet x acute stress exposure). A) In males, undergoing the FST resulted in significantly increased corticosterone. In fructose-fed males, corticosterone was reduced at baseline and following the FST. B) In females, corticosterone was elevated by acute stress exposure but was not altered by diet. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05.