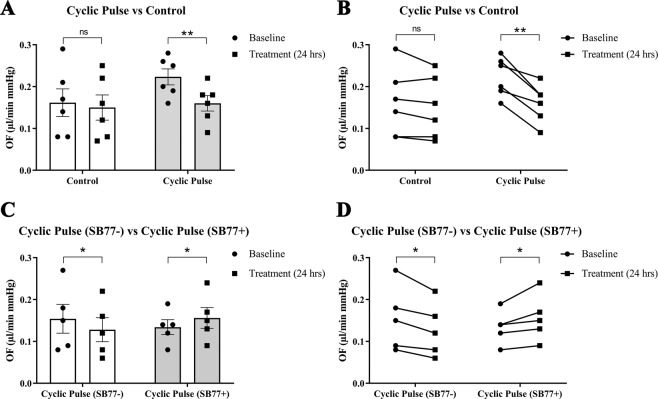
Figure 1.
The effect of cyclic pulsations on aqueous outflow facility. The experimental anterior segment received IOP pulsations for 8 h. (A) The presence of experimentally induced cyclic mechanical stress significantly reduced the aqueous outflow facility as compared to its control (p = 0.003 (BL vs 24 hours); n = 6 pairs). Individual data points (black color dots) are indicated on the bar graph representing mean ± SEM. (B) Pairwise comparison between baseline and post cyclic pulsations for all treated pairs of eyes is represented. (C) Treatment with SB77 showed a significant increase in the outflow facility as compared to its control (p = 0.05 (BL vs 24 hours); n = 5 pairs). Individual data points (black color dots) are indicated on the bar graph representing mean ± SEM. **p < 0.005; *p < 0.05; Paired t-test. (D) Pairwise comparison of each pair of eyes received cyclic IOP pulsations in presence or absence of SB77 treatment is represented.