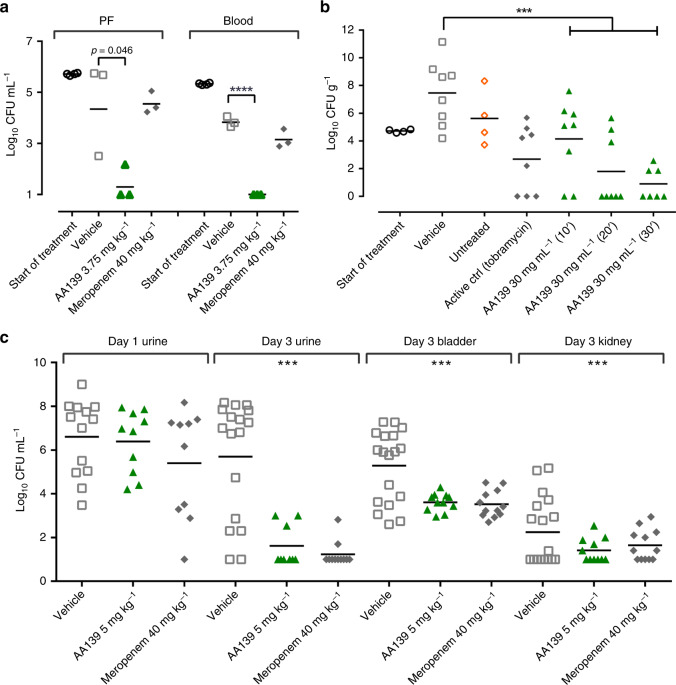
Fig. 5. In vivo peritonitis, pneumonia and UTI murine models for AA139.
a Peritonitis model dosed at 3.75 mg kg−1 against MDR E. coli AID#172 (inoculated in the lateral lower quadrant of the abdomen by single I.V dose) with CFU mL−1 measured in the peritoneal fluid (PF) and the blood after 5 h post infection (n = 4 for start of treatment groups and n = 3 for other groups). b P. aeruginosa pneumonia model treated with aerosolized AA139 for 10, 20, or 30 min duration in an aerosol exposure chamber at 2, 12, and 24 h post infection. The bacterial load (CFU g−1 lung tissue) was measured at 34 h post infection (n = 4 for start of treatment group, n = 7 for AA139 30 min treatment group and n = 8 for other groups). c Bacterial load (CFU mL−1) in the urine of UTI murine model infected with ESBL producing E. coli DSA 443 before treatment (day 1), and bacterial load (CFU mL−1) in the urine, bladder, and kidney after last treatment (day 3). Animals were treated twice-daily with AA139 at 5 mg kg−1 or meropenem at 40 mg kg−1 i.v. (n = 12). Horizontal bar indicates geometric mean burden of each treatment. Statistical comparison performed with Prism 8 using one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, and all differences between means with p ≤ 0.05 are indicated: ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001. Source data are provided as a source data file.