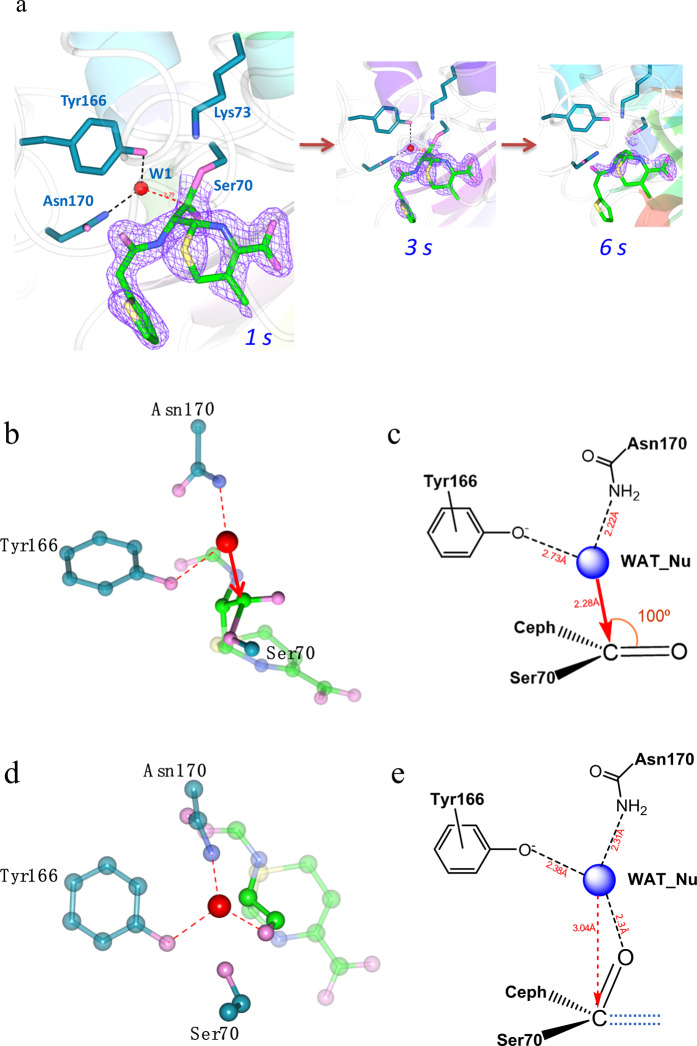
Figure 5.
Structures of deacylation intermediates reveal critical factors to activate the catalytic water molecule. (a) The time-dependent profile of in crystallo deacylation process as depicted by three structures captured at 1, 3 and 6 seconds respectively. The Fo-Fc omit map (purple) is drawn in mesh format and contoured at 2.0 σ to highlight the disappearance of the acyl adduct. (b) The catalytically competent conformation of the deacylation-3s structure shows WAT_Nu poised with perfect geometry to carry out nucleophilic attack on the acyl adduct. (c) Scheme presentation of the Bürgi-Dunitz trajectory for this conformation. (d) The catalytically incompetent conformation of the deacylation-3s structure reveals a hydrogen bond between WAT_Nu and the “tilted” carbonyl oxygen of the acyl adduct. (e) Scheme presentation of (d). The dashed lines represent the orientation of the carbonyl oxygen in the catalytically competent conformation in (c).