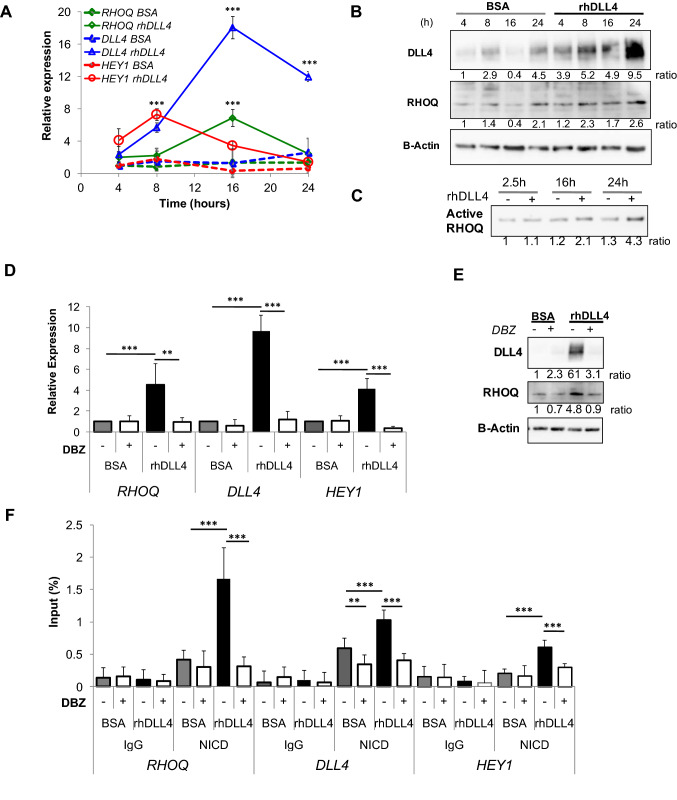
Fig. 1.
RHOQ is induced by DLL4/Notch signalling in vitro. HUVECs were grown on BSA or rhDLL4-coated plates, harvested at indicated time points and changes in RHOQ and DLL4/Notch targets were assessed by a QPCR or b by western blotting. c Active RHOQ status following GTPase pull down assay and magnitude of active RHOQ was detected by western blotting. Changes in DLL4/Notch target expression following 16 h incubation with DBZ (20 nM) compared to DMSO equivalent controls was assessed by either. d QPCR, normalised to BSA DMSO control, or e by western blotting, or f cells were fixed and analysed for NICD bound to Notch promoter binding site for RHOQ, compared to that of DLL4 and HEY1 by chromatin immunoprecipitation. β-Actin as a loading control and densitometry was performed on western blots. Densitometry ratios were expressed relative to the first BSA control sample (Error bars = S.D. Key: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001 one-way ANOVA or unpaired Student’s t-test comparing two data groups; data representative of n = 3 independent experiments)