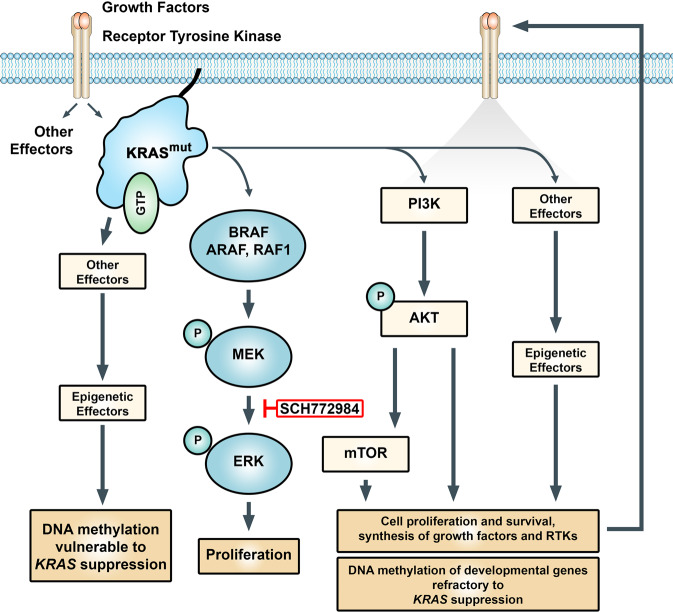
Figure 6.
Model showing epigenetic regulation of developmental genes by mutant KRAS. Activating KRAS mutations lead to persistant induction of effector pathways that drive the cancer phenotype including the differential DNA methylation of genes involved in development and differentiation. In some cell lines, effector pathways such as PI3K and others, are able to maintain their abberant activity independent of KRAS signaling. As a consequence of feed forward loops initiated by mutant KRAS, kinome reprogramming, or the establishment of stable epigenetic patterns, the majority of DNA methylation changes associated with mutant KRAS activity remains refractory to KRAS suppression. However, independent of the changes in DNA methylation, KRAS knockdown and ERK inhibition still both lead to growth arrest in KRAS driven cell lines. SCH772984, type I and type II ERK inhibitor.