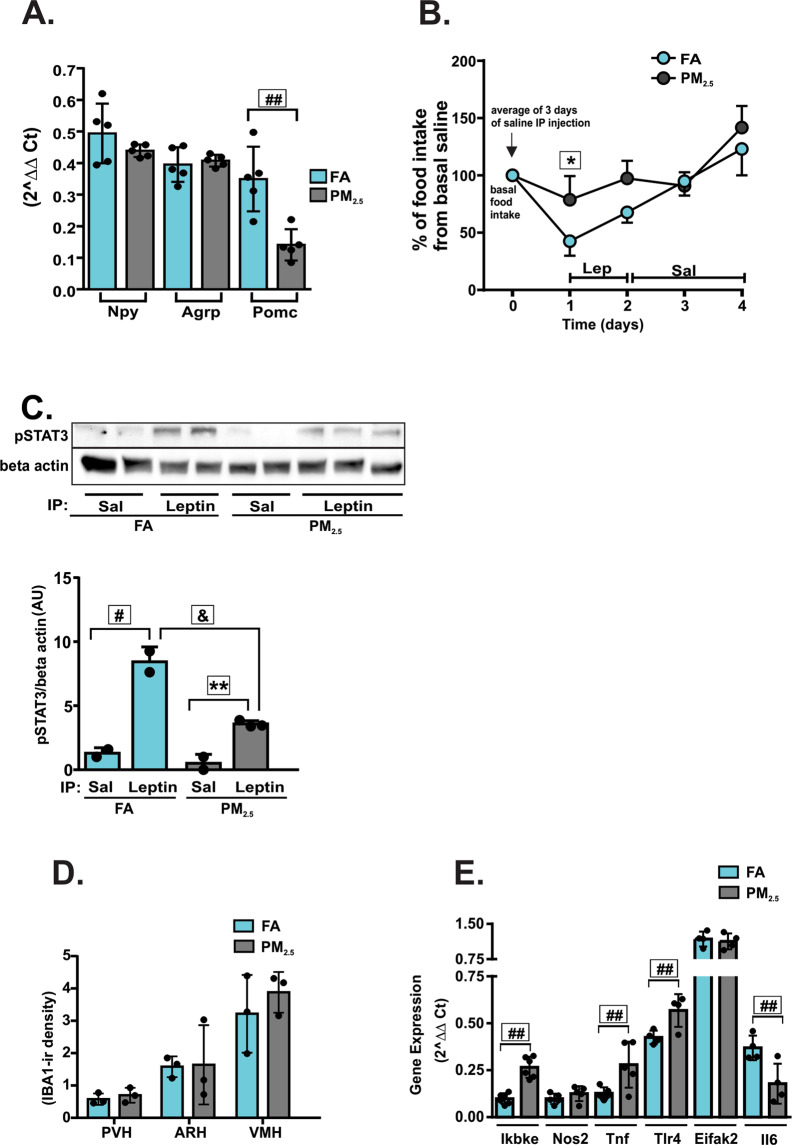
Figure 3.
Long-term exposure to PM2.5 impairs leptin sensitivity, alters the expression of hypothalamic neuropeptides and increases inflammatory mediators. Mice were exposed to particulate matter less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter (PM2.5) or filtered air (FA) for 12 weeks. (A) Npy (neuropeptide Y), Agrp (Agouti-related protein) and Pomc (Pro-opiomelanocortin) gene expression in the hypothalamus after 24 h of fasting n = 5 for each group. (B) Intraperitoneal (IP) leptin sensitivity test, the results of food intake during the 3 days of leptin injection was compared to the basal FI for each mouse and were expressed as a percent of the basal (saline) food intake for each mouse n = 4 for each group. (C) STAT3 phosphorylation (Arbitrary Units) in response to IP leptin or saline injection was measured in the hypothalamus of overnight fasted mice; n = 2 for FA (saline, leptin) and PM2.5 (saline) groups and n = 3 for PM2.5 (leptin) group (full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1A). (D) Iba-1-ir density expression in hypothalamic nuclei and (E) hypothalamic gene expression of mice exposed to FA or PM2.5 for 12 weeks n = 4–6. Abbreviations: Ikbke - inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon; Nos2 - inducible nitric oxide synthase 2; Tnf - Tumor necrosis factor alpha; Tlr4 - Toll-like receptor 4; Eifak2 - Eukaryotic translation initiation factor-α kinase 2; Il6 - Interleukin 6. All of the mice studied were 6–8 weeks of age. Data were presented as the mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA (Panels A and C) and two-way ANOVA (Panel B) followed by a Tukey post hoc test were used for the statistical analysis *P < 0.05 vs FA; #P < 0.05 vs. FA leptin; &P < 0.05 vs. PM2.5 leptin; **P < 0.05 vs PM2.5 leptin; ##P < 0.05 vs FA (same gene).